A PN-junction diode can be operated in both forward and reverse biassed modes, as we know. A Zener diode is a type of diode that operates well in reverse biassed conditions. In a reverse biassed state, both Zener and avalanche breakdown occur. The nature of operations differs significantly between Zener and avalanche breakdown.
If the applied voltage is greater than the threshold voltage, we may see the flow of the current of flow charge carriers in the forward biassed situation (which is also known as the barrier potential). The major flow of current in the reverse biassed condition is due to minority charge carriers; this saturation current will not change up to a certain voltage; however, after a certain voltage limit, we notice the flow of current in the reverse direction; this region is known as the breakdown region, and the applied potential is known as the Breakdown potential. The avalanche effect is the name for this phenomenon.
Zener Breakdown and Avalanche Breakdown
Let us first define avalanche breakdown and Zener breakdown separately before moving on to the Zener breakdown vs avalanche breakdown.
What is Avalanche Breakdown?
The current reverse biassed condition is primarily owing to the minority charge carriers, as we know. The breadth of the depletion region widens as the applied voltage rises, resulting in more stationary charged carriers in the depletion region. A strong electric field will emerge in the depletion zone as a result of the increased immobile charge carriers, and the minority charge carriers present in the depletion region will be accelerated, allowing them to tunnel through the depletion region.
The accelerated charge carriers collide with the atoms present and accumulate enough kinetic energy to destroy the valence electrons when the applied voltage exceeds the breakdown zone or the breakdown potential. Two free electrons are produced as a result of the collision. These two free electrons can crash with additional atoms, resulting in four free electrons. This collision can continue, resulting in a significant increase in charge carriers in the depletion region. We will witness a sharp increase in the reverse saturation current as a result of the additional charge carriers.
The Avalanche effect is named after the voltage at which the avalanche effect appears, and the breakdown voltage is the voltage at which the avalanche effect appears. Impact ionisation causes the avalanche breakdown effect.
What is Zener Breakdown?
To protect the equipment from damage, this region of operation must be avoided for typical diodes. The Zener diode, for example, is a unique type of diode developed specifically to work in this zone. The Zener diode is a form of PN-junction diode that functions in a reverse biassed state. The breakdown operation in the Zener diode, however, differs from that of the avalanche breakdown; this breakdown is known as the Zener breakdown.
The P and n regions of Zener diodes, unlike conventional PN-junction diodes, are extensively doped; in other words, the number of impurity atoms in the Zener diode will be higher than in a regular PN-junction diode. There will be a huge number of free charge carriers due to the existence of large impurity charge carriers. The breadth of the depletion region will be narrowed as a result of substantial doping, resulting in an extremely strong electric field. Many free electrons are created as a result of the strong electric field, and they can readily tunnel through the depletion area, resulting in the reverse saturation current.
The Zener breakdown effect is the name given to this phenomenon, and the voltage at which it occurs is called the Zener breakdown voltage. This is the primary distinction between Zener and avalanche breakdowns, and one can now easily compare Zener and avalanche breakdowns.
Difference Between Avalanche and Zener Breakdown
Let’s begin by defining the differences between Zener and avalanche breakdown. A few areas where Zener and avalanche breakdown differs are listed below. This question may also be posed to distinguish between Zener and avalanche breakdown mechanisms; nevertheless, one should not become confused while replying.
These are significant avalanche and Zener breakdown distinctions.
Breakdown Mechanism
When the reverse bias on a p-n junction is increased, the connection breaks down, and the reverse current rapidly climbs to a magnitude limited only by the external resistance in series. The reverse bias voltage’s breakdown voltage is a specific value (vz). Increase the reverse current by a small amount after the breakdown. The thickness of the depletion layer determines the breakdown voltage. The width of the depletion layer is determined by the doping level. With the help of this post, we have attempted to explain the concept of Zener Breakdown and Avalanche Breakdown Mechanism in detail as Basic Electronics Notes.
Breakdown Characteristic Graph
The image below shows a graphical illustration of the Avalanche and Zener breakdown.
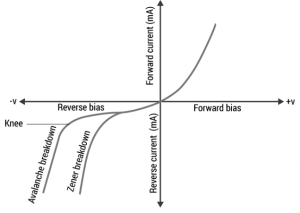
Fig: breakdown characteristic
Conclusion
The Zener effect is a form of electrical breakdown discovered by Clarence Melvin Zener and used most notably in the suitably called Zener diode. It happens in a reverse biassed p-n diode when the electric field allows electrons to tunnel from the valence to the conduction band of a semiconductor, resulting in a large number of free minority carriers that cause the reverse current to spike.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






