To make alkyl fluorides from alkyl chlorides or alkyl bromides, the Swarts reaction is commonly used. Heating alkyl chloride/bromide in the presence of heavy metal fluoride achieves this (silver fluoride or mercurous fluoride for example). If sodium fluoride or potassium fluoride are employed, the reaction will proceed, but the yield will be much reduced. Frederic Jean Edmond Swarts was the first to report this phenomenon in 1892. Swats fluorination is another name for the swarts reaction. Chlorine is most typically replaced by fluorine in organic compounds in Swarts fluorination with the use of antimony trifluoride in the presence of antimony salts, where its oxidation state is +5.
Swarts Reagent
Antimony trifluoride (SbF3) is commonly used to replace chlorines with fluorines in the presence of Sb salts in which antimony has an oxidation state of +5. (SbCl5) Swarts reagent is a mixture of antimony trifluoride (SbF3) and chlorine (Cl2).
Mechanism of Swarts Reaction
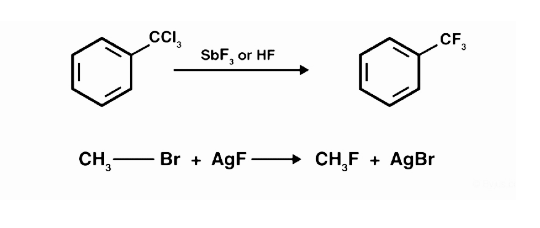
The Swarts reaction has a straightforward mechanism: the metal fluorine link is broken, and a new carbon-fluorine bond is generated. The metal has created a connection with the chlorine or bromine atoms that have been displaced. Swarts reagent is an antimony trifluoride and chlorine mixture. Swarts’ law states that after fluorination, the fluoride produced has a lower boiling point than the comparable chloride.
Chlorinated hydrocarbons can also be combined with metallic fluorides to form fluorinated hydrocarbons.
As a result, Swarts fluorination can be used to completely replace chlorine or bromine with fluorine in alkyl chlorides/bromides. A variant of the reaction is critical in the formation of Freons. In this variation, anhydrous hydrogen fluoride is fluoridated in the presence of antimony salts (in catalytic quantities), with antimony having oxidation levels of +3 and +5.
Applications
- Alkyl fluorides are made using this process. Freons are made using a variation of this process. Fluorinated aliphatic organic compounds are known as freons.
- Fluorination is carried out in this form utilising anhydrous hydrogen fluoride (HF) in the presence of Sb salts with oxidation states of +3 and +5.
Finkelstein Reaction
The Finkelstein reaction is an SN2 reaction (Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular reaction) in which one halogen atom is replaced by another. It is named after German chemist Hans Finkelstein. Although it is an equilibrium reaction, it can be accelerated by taking advantage of the differential solubility of halide salts or by utilising a sufficient amount of the halide salt.
Method
The standard Finkelstein reaction involves treating an alkyl chloride or alkyl bromide with a solution of sodium iodide in acetone to convert it to an alkyl iodide. Unlike sodium chloride and sodium bromide, sodium iodide dissolves in acetone. Due to the precipitation of the poorly soluble NaCl or NaBr, mass action drives the reaction toward products.
Uses for Analysis
The ease with which alkyl halides undergo the Finkelstein reaction varies substantially. The reaction is effective for primary halides (excluding neopentyl) and especially for allyl, benzyl, and -carbonyl halides. Secondary halides are far less reactive than primary halides. With the exception of alkyl iodides, which yield the same product when substituted, vinyl, aryl, and tertiary alkyl halides are unreactive; as a result, The reaction of NaI in acetone can be used to determine which of the aforementioned classes an unknown alkyl halide belongs to using a qualitative test.
Swarts and Finkelstein Reaction: Difference
Alkyl halide synthesis is linked to both the Finkelstein and Swarts reactions. The exchange of halides between organic compounds (or organic and inorganic compounds) to produce new alkyl halides is described by these reactions. The main difference between the Finkelstein and Swarts reactions is that the Finkelstein process produces alkyl iodide, while the Swarts reaction produces alkyl fluoride. Primary halides, secondary halides, allyl halides, and benzyl halides are all acceptable reactants for the Finkelstein reaction, while tertiary reactions, vinyl, and aryl halides are not. Alkyl chloride or alkyl bromide, as well as a fluorinating agent such as antimony fluoride, are the reactants in the Swarts reaction.
Related Links:
Conclusion
Alkyl halide synthesis is linked to Finkelstein and Swarts reactions. The exchange of halides between organic compounds (or organic and inorganic compounds) to produce new alkyl halides is described by these reactions. The main difference between the Finkelstein and Swarts reactions is that the Finkelstein process produces alkyl iodide, while the Swarts reaction produces alkyl fluoride.
Related Pages
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




