According to the work-energy theorem, the change in the kinetic energy of a body is similar to the network done by the forces acting on it. The work-energy theorem can also be derived from Issac Newton’s second law.
To state the work-energy theorem, we also need to understand the concept of work and energy. Both work and energy are closely associated with each other. When we try to move an object, we also change the object’s energy. Energy is spent in doing work. We can describe energy as the ability to do any work.
Work
A work is said to be done when an application of force causes the displacement of an object. The SI unit in which work is determined is called Joules, i.e., 1 J = 1 N ⋅ m = 1 kg ⋅ m2/s2. Work is defined as the scalar quality as it only has magnitude and has no directions.
Mathematical formula: (F cos θ )d = F.d
The SI unit of the work is Joule (J). Whereas in the CGS system, the unit of work is erg. The dimensional formula of work is ML2T-2.
For example: Suppose you use thread to pull a curtain over the floor, consider that the curtain is your system, and the force you are applying to pull the curtain is a type of external force.
So, the amount of the work you are doing is equal to the force you are using to pull the curtain times the distance you moved it.
According to the work equation, if there is no displacement, then work done is 0, which means no work has been done. It implies that there is no work is done when:-
- Force = zero
- the displacement = 0
- Force and displacement make 90-degree angles or mutually perpendicular.
Energy
Kinetic energy is also known as the energy of motion. Any moving object has kinetic energy in it.
Potential energy is also called stored energy, and it has several forms. For example, gravitational potential energy is stored in the object, and it is due to the object’s position on the earth’s surface. You must be familiar with roller coaster rides. When a roller coaster is on the top, it has the potential gravitational energy to go down.
This can be represented mathematically by the work-energy theorem.
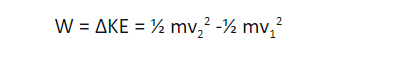
v2 and v1 in this theorem refer to the final and initial velocity of the object.
The work-energy theorem is derived from Newton’s second law of motion and the force applied to a particle. The immediate power added to the system is determined by computing the scalar product of the forces with the particle’s velocity.
Work-energy theorem derivation
Work-Energy Theorem can be represented mathematically by the work-energy theorem.
![]()
v2 and v1 in this theorem refer to the final and initial velocity of the object.
The work-energy theorem is derived from Newton’s second law of motion and the force applied to a particle. The immediate power added to the system is determined by computing the scalar product of the forces with the particle’s velocity.
When the resulting force F is constant in size and direction and parallel to the particle’s movement, we can obtain the equation of the work-energy theorem. The particle follows a straight route and accelerates at a constant rate.
The equation F = ma expresses the relationship between net force and acceleration, and the particle’s displacement d may be determined using Newton’s 2nd rule of movement:

The work-energy theorem is derived in this way. As a result, we can conclude that the work done on an object equals the change in the object’s kinetic energy.
Conclusion
From the article, we can conclude that how work and energy are linked together via the work energy theorem and we can also understand the application of the work energy principle. According to the work-energy theorem, the change in the kinetic energy of a body is equal to the total work done by the forces acting on it.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






