In our daily routine, we have come across instances where heat transfer has played a vital role. For example, when we bring the ice outside from the freezer, it starts to melt during the hot summer days. Since the temperature outside the freezer is higher than the freezing point of water, the heat transfer occurs from the atmosphere to the ice. Due to the transfer of heat, the solid ice is converted into liquid water.
There are three different ways of heat transfer – conduction, convection, and radiation. This article will discuss conduction and the various factors that affect the conduction process.
What is Conduction?
Conduction is the transfer of heat from the hot end to the cold end of an object through molecular collisions. The transfer of heat from one end of the material to the other takes place due to the vibration of molecules present in the material. When the material is heated to a certain temperature, the atoms gain energy, which makes them vibrate. The vibrating molecules then collide with the adjacent molecules present in the material. The collision of molecules leads to the transfer of energy from one molecule to another.
For instance, when we keep a frying pan on the gas stove, the flame heats the utensil. Now, if the handle of the pan doesn’t have an insulating plastic cover on it, holding the pan will become extremely difficult because, due to conduction, the heat will transfer from the base of the pan to the handle of the utensil. Moreover, when the pan is removed from the flame and kept aside, the temperature of the pan decreases. This mainly occurs due to heat transfer from the hot pan to the surroundings.
Conductors and Insulators
To answer what is conduction, it is essential to understand the heat transfer in solids. However, this doesn’t mean that every solid is a good conductor. There are some solids that are poor in the conductance of heat.
Materials that can transfer heat effectively are called conductors of heat. Some of the conductors of heat are aluminium, steel, and copper. The materials that are not capable of conducting heat are called insulators. Some of the common insulators are plastic, rubber, ceramics, wood, etc.
Factors That Affect Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is defined as the ability of a material to conduct or transfer heat. Conductivity is generally represented by the letter K. Conduction is responsible for different operations such as cooking food, heating rooms using domestic household heaters, etc. But the effectiveness of the conduction process depends on the other factors of thermal conductivity.
The factors affecting thermal conductivity are as follows:
Material of the Object
One of the crucial factors that contribute to conduction is thermal conductivity. The material used for conduction affects the rate at which energy flows between two regions. To get more conductance in a process, it is advisable that you use a higher thermal conductivity material.
Length of the Object
Thermal conductivity is inversely proportional to the length of the object. Therefore, an object that is smaller in length will conduct heat at a faster pace than a more extended object. Thus, as the length increases, the heat transfer rate decreases.
Difference in Temperature
Heat transfer works on the principle of temperature difference. Therefore, if the temperature difference between two objects is more, the heat transfer will be quicker. Thus, with the increase in temperature, the conductivity increases.
Type of Cross-section
The type of cross-section also affects the rate of heat transfer. If a section is hollow or round, the conductivity of the object will be different because the area of the object will be different.
Example
The formula for thermal conductivity is:

Now, let’s take an example.
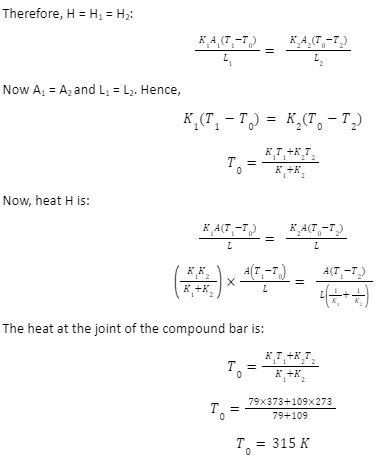
An iron bar and a brass bar have the following characteristics, as mentioned below. The free ends of the steel and brass bars are maintained at 373K and 273K. Find the temperature at the joint of the bars.
Given:
Length of the iron bar (L1) = 0.1m
Length of brass bar (L2) = 0.1m
Area of iron bar (A1) = 0.02 m2
Thermal conductivity of Iron (K1) = 79 W/mk
Area of brass bar (A2) = 0.02 m2
Thermal Conductivity of Brass (K2) = 109 W/mk
In the case of the steady-state condition, the heat (H1) through the iron bar will be the same as that of the brass bar, i.e., H2.
Conclusion
To understand what conduction is, it is extremely vital to understand the working of different natural processes such as the rain cycle and sea breeze. Conduction plays a significant role in the development of the sea breeze. Since solids get heated quickly in comparison to the fluids, the air present near them heats up and gets lower in density. The lower density air then rises, and a vacuum is produced. Now, this vacuum is replaced by cool air, which is present over the water density because water is a bad conductor of heat. Through the phenomenon of sea breeze, we can understand the importance of conduction in real-life scenarios.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






