Periodic waves are employed in physics to describe the propagation of energy in the form of light, sound, wind, or any other kind of energy. This wave is described as a function of sinusoidal waves since it is a smooth periodic oscillation. Previously, light was described as a collection of extremely small particles with no mass. It was also hypothesised that the particles of various coloured photons differed. Based on this idea and the fact that light particles are elastic in nature, all other natural phenomena of light such as reflection, refraction, and diffraction were recognised.
Christian Huygens launched a significant scientific revolution in the 17th century. He claimed that light is actually a type of energy that travels in waves. He explained it by claiming that any point source of light emits light waves simultaneously in all directions in three dimensions. Under the impact of wave energy, the particles in its environment vibrate on a regular basis. The points of a certain place are present at the same time phase in this sort of propagation. A wavefront is the plane generated by this cluster of points or particles in the same phase.
We will talk about how light is in the form of a wave and what is the contribution of wavefront in it, in the coming paragraphs, which are like this.
What is Wave Front?
The set of all points in a medium where the wave is at the same phase is known as a wavefront. This could be the location of all crests, troughs, or any other phase in between. Wavefronts are useful for depicting the movement of waves in two dimensions. On a wavefront, the distance between two lines is exactly one wavelength. A wavefront is an imaginary surface that represents a wave’s corresponding points vibrating in unison. The set or locus of all the points in the same phase is called a wavefront. Plane wavefronts, spherical wavefronts, and cylindrical wavefronts are the three forms of wavefronts. We’ll go through each of these sorts of wavefronts in detail in the next sections.
Types of Wavefront
The numerous forms of wavefronts are determined by the path taken by particles originating from a source., here some types of wavefront are described, which are as follows;
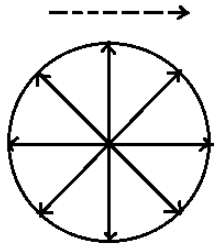
Spherical wavefront- It’s a circular wavefront generated by a single point of light. Because the locus of all points at the same distance from the point source is the same. Examples can be electromagnetic waves in a vacuum, rings produced by a stone placed in water, etc.
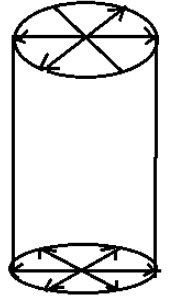
Cylindrical wavefront- A cylindrical wavefront is created when the light source is linear in shape. This is due to the fact that all equidistant points from the linear source are found on the surface of a cylinder. It refers to the rays of light coming out of the lens, when the rays of these lenses fall on the other lens, These rays take the form of a cylinder at the point where they meet.
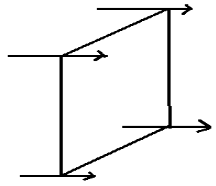
Plane Wavefront- A plane wavefront is a small piece of a spherical or cylindrical wavefront emerging from a distant source that appears flat. The biggest example of this is the rays
Application of Wavefront
Wavefront technology is mostly utilized in the medical profession to cure eyes. It is used to improve visual acuity as well as shape the cornea. Wavefront technology helps to lessen the negative effects of standard LASIK. LASIK refers to Laser-Assisted In-Situ. Wavefront-guided LASIK procedure uses in-depth, wavefront-generated measurements of how light waves take a trip through your eyes and fall upon the retina, to create a laser treatment that is entirely customised for your eye anatomy and vision correction needs.Astigmatism and hypermetropia, in addition to myopia or nearsightedness, are proving to be more effective in treatment today.
Conclusion
The imaginary wave front represents the matching points of a wave that vibrate in unison. When identical waves from the same source move through a homogeneous medium, their peaks and troughs are in phase at any given time; that is, they have completed equal degrees of their cyclic motion, and all surfaces drawn through all locations of the same phase form a wave front. As we read here. We also utilise a wavefront as a sensor, which measures wavefront aberration in a coherent signal to represent the optical quality of an optical system. Wavefront techniques are also valuable in areas such as adaptive optics and optical metrology.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






