The resistance of a fluid (liquid or gas) to a change in shape or movement of adjacent sections relative to one another is called viscosity. The term “viscosity” refers to the resistance to flow.
The mass of a material substance per unit volume is called Density. Density is calculated using the formula d=M/V, where d represent density, M is mass and V is volume. The density of a substance is usually expressed in grams per cm. Water, for example, has a density of 1 grams per cubic cm, but the density of the Earth is 5.51gm per cm. The kilogram per cubic m unit of measurement is also used to express density (in m-kilogram-second or SI units)
Viscosity and Density
The kilogram (kg) is the standard unit of mass in the SI system of units, while the cubic meter is the standard unit of volume and the second is the standard unit of time.
Density p
A fluid’s density is calculated by dividing the mass of the fluid by the volume of the fluid. The standard unit of density is kg per cubic m. p=kg/m3 .Water has a density of 998 kg/m 3 at a temperature of20℃.
The density of a fluid is also referred to as Relative Density. The fluid density is divided by 1000kg/m3to get relative density.
The relative density of water at 20°Celsius is 0.998
Dynamic Viscosity μ
The viscosity of a fluid describes its resistance to flow. Dynamic viscosity is calculated by dividing the rate of shear strain by the shear tension (also known as absolute viscosity). The units of dynamic viscosity are as follows: x time = area / force. The Pascal unit (Pa) is used to measure pressure or stress, which is defined as force per unit area.
To define dynamic viscosity, mix this unit with time (sec).
μ=Pa∙s
1.00Pa∙s=10 Poise=1000 Centipoise
Because water has a viscosity of 1.002 centipoise at 20℃, the term centipoise (cP) is widely used to nature dynamic viscosity. For calculation, this value must be translated back to 1.002×10-3 Pais.
Kinematic Viscosity v
The flow of a known volume of fluid from a viscosity measurement cup is sometimes used to determine viscosity. The timings can be used with a formula to calculate the fluid’s kinematic viscosity in Centistokes(cSt).The head of fluid is the propelling force that propels the fluid out of the cup. This fluid head is also a part of the equation that determines the fluid’s volume. The fluid head term is removed from the calculations, leaving the units of Kinematic viscosity as area / time.
v=m2/s
1.0m2s=1000 Stokes=1000000 Centistokes
Water has a viscosity of 1.004×10-6m2 at a temperature of 20℃
1.004000 Centistokes is the result. For calculation, this number must be translated back to1.004×10-6m2. By dividing the dynamic viscosity by the fluid density, the kinematic viscosity can be calculated.
Kinematic Viscosity and Dynamic Viscosity Relationship
Kinematic Viscosity = Dynamic Viscosity/Density
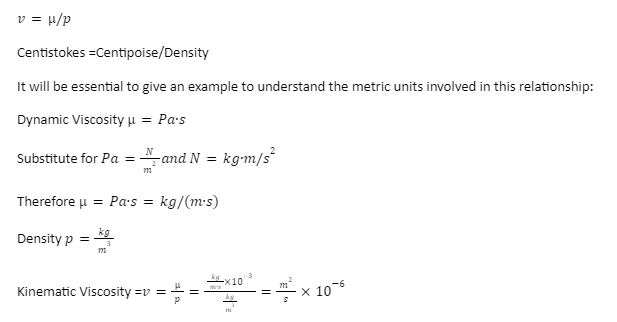
Viscosity and Density (Imperial Units)
The pound (Ib)is the standard unit of weight in the Imperial system, while the cubic foot is the standard unit of volume and the second is the standard unit of time. The slug is the standard unit of mass. When a force of one pound (Ibf)is applied to the mass, it accelerates by one foot per second. Gravitational acceleration(g) is 32.174 feet per second per second. The weight (Ib)of a fluid must be divided by 32.174 to find its mass.
Density p
Normally, density is measured in mass (slugs) per cubic foot. A fluid’s weight is measured in pounds per cubic foot.

Dynamic Viscosity
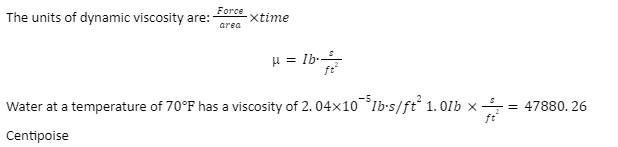
Kinematic Viscosity and Dynamic Viscosity Relationship
Kinematic Viscosity = Dynamic Viscosity / Density
v=μ/p
The imperial unit of Kinematic Viscosity are ft2s
To understand the imperial units involved in this relationship it will be necessary to use an example:

Conclusion
Viscosity refers to a fluid’s (liquid or gas) resistance to a change in shape or movement of adjacent parts relative to one another. The resistance to flow is referred to as viscosity.
In the SI system of unit, the kilogram ((kg) is the standard unit of mass, while the cubic m is the standard unit of volume and the second is the standard unit of time.
The viscosity of a fluid describes its resistance to flow. Dynamic viscosity is calculated by dividing the rate of shear strain by the shear tension (also known as absolute viscosity). The units of dynamic viscosity are as follows: X time=area/force
When determining viscosity, a known volume of fluid is flowed from a viscosity measurement cup. The timings can be used to compute the fluid’s kinematic viscosity in Centistokes using a formula cSt. The force that propels the fluid out of the cup is known as the head of fluid. This fluid head is also a factor in determining the volume of a fluid.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






