A force is a push or pull that occurs as a result of one object’s interaction with another object. Forces come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Earlier in this lesson, a number of force types were classified into two categories based on whether the force was caused by touch or non-contact between the two interdependent parts.
Force
The motion of an object is stopped or tends to be stopped by a force that moves or tends to move. A force can also modify the direction of an object’s motion. It has the ability to change the shape or size of the body on which it is working. As a vector quantity, it possesses both magnitude and direction.
Real forces are described in classical physics by a series of axioms called Newton’s laws of motion, which are applied to an inertial reference frame. The resultant force F acting on a body of constant mass m is equal to ma, where an is the acceleration of a, according to Newton’s second law. They are vector quantities.
There are long-range and short-range forces. Long-range forces, such as gravitation and the Coulomb force, decay faster than the inverse square of the distance, whereas short-range forces, such as those within the atomic nucleus and between molecules, decay rapidly than the inverse fourth power of the distance. Short-range forces in a condensed body can be shown to be modest at distances not much greater than those of close friends nearby.
SI units of Force
The newton, abbreviated N, is the SI unit of force. “One newton (1 N) is the force that creates an acceleration of one meter per second square in a body of mass one kilogram, according to Newton’s second law of motion. As a result, a force of one newton can be written as:
1 N=1 kg1ms-²
1N=1kgms-²
Types of Forces
- Contact forces
- Non-contact forces or at a distance force
Contact forces
Two objects come into physical touch and one exerts a force on the other, resulting in those forces.
Examples:
- Stretching of the spring of a balance
- The pushing of a pram
- Pushing the door
- Kicking of a football
- Hitting the ball are some examples of contact forces.
Types of contact forces
- Applied force
- Normal force
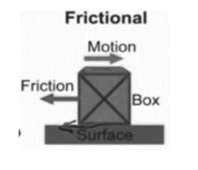
- Frictional force
- Tension force
- Air resistance force
- Spring force
Applied Force
An applied force is a force that is applied to an object by a person or another object. The object is subjected to an applied force when a person moves a desk across the room. The applied force is the force applied to the desk mostly by person.
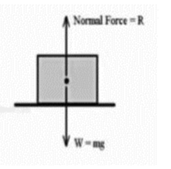
Normal Force
It’s a surface-to-surface contact interaction force. It always acts out of the surface and perpendicular to the surfaces. It is derived from the tiny deformation of molecules in the shape of a spring system.
Frictional Force
The normal force is the support force applied to an object in contact with another object that is steady. For example, If a book is sitting on a surface, the surface is exerting an upward force on the book in order to sustain its weight. A normal force is sometimes exerted horizontally between two objects in touch with one other. When a person leans against a wall, for example, the wall pulls horizontally on the person.
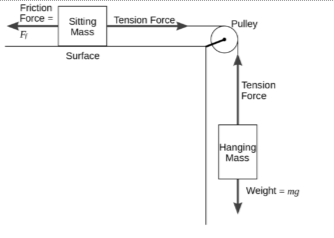
Tension Force
When forces working from opposite ends pull a string, rope, cable, or wire tight, the tension force is conveyed through the string, rope, cable, or wire. The tension force is directed along the wire’s length, pulling evenly on the objects at the wire’s opposite ends.
Air Resistance Force
Air resistance force is the force that acts in the opposing direction of motion through a gas. It rises in proportion to the increase in gas velocity. It also gets bigger when the area normal to the motion gets bigger.
Spring Force
The spring force is the force exerted by a compressed or expanded spring on anything attached to it. An object that compresses or extends a spring is always subjected to a force that recovers the object to its rest or equilibrium state. The size of the force is precisely proportional to the degree of stretch or compression of most springs (particularly, those that are claimed to obey “Hooke’s Law”).

Noncontact Forces
Those forces act through the space between the two items rather than through actual contact between them.
Examples:
- Gravitational force
- Electromagnetic force
- Weak nuclear force
- Strong nuclear force
Gravitational force of attraction
The attraction of another item to the earth, moon, or other massively large object is known as gravity. This is, by definition, the object’s weight. All objects on Earth are attracted “downward” to the earth’s core by gravity. According to the equation, an object’s weight is always equal to the gravitational acceleration force.
w=m × g
Electromagnetic force
The electromagnetic force is responsible for the binding of atoms and the construction of solids, and it encompasses basic electric and magnetic interactions.
Weak nuclear force
Among the most fundamental particles, the weak nuclear force drives certain radioactive decay processes and reactions.
Strong nuclear force
The nucleus is held together by the strong force, which operates between fundamental particles.
Ways to measure force
The dynamic method of measuring force involves applying acceleration to a standard body by tugging on it using a stretched spring. Although useful for definition, it is not necessarily a viable approach for force measurement. (Acceleration is difficult to quantify.)
Another approach for measuring forces is to measure the change in shape or size of a body (such as a spring) on which the force is exerted when it is not accelerated. This is termed as the static method of measuring devices.
Conclusion
A force that moves or tends to move stops or tends to stop the motion of an object. A force can also change the direction of motion of an object.
There are following types of forces which are given below;
- Applied force
- Normal force
- Frictional force
- Tension force
- Air resistance force
- Spring force
Gravitational force is given as
w=m ×g
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






