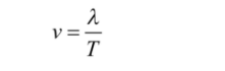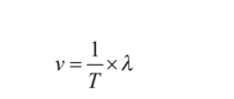A wave is the movement that occurs in a medium from one point to another when a body comes in contact with it. For example, consider that when you throw a rock or stone into a river, patterns are created in a circular motion through the point where the rock hits the water. Here the stone is the body and the water is the medium, and the patterns that appear on the water’s surface are waves.
There are two types of waves which are Transverse and Longitudinal Waves.
Longitudinal Waves
A wave consisting of a vibration or periodic disturbance occurring in the same direction as the wave motion. When you compress and release one end of the coil spring, you will experience a compression wave traveling along the length of it, which means stretching follows. The coil of spring has a point which moves with the wave and returns in the same way. While on returning, it starts from the neutral position and then reverses its movement again. The movement of sound through air results in compression of the gas in the direction that sound waves travel as they oscillate back and forth. Seismic waves that are primarily are also longitudinal.
Longitudinal waves are defined as the waves in which the displacement of the medium is in the same direction of the movement of the wave.
Transverse Waves
Transverse wave is defined as a wave in which the particles of the medium move in the direction perpendicular to the wave. For example, consider When a string is placed horizontally in a room and a movement is introduced to the left end of the wave of string, then the energy moving on the string (ropes) moves from left to right, which causes simultaneous up and down movement on the string. This type of wave generated is a transverse wave. The characteristic of a transverse wave is that the motion of the particle is normal to the motion of the wave.
Speed of Transverse Waves
Transverse waves consist of crests and troughs. The peak is the highest point of the wave and the trough is the lowest or bottom of the wave.
The speed of a transverse wave is determined by dividing the distance with time taken by the transverse wave to travel.
Therefore,
And,
Therefore,
Here,
v = velocity of wave
T = time
f = frequency
λ= wavelength
Terms used in Transverse Waves
Crest
The wave crest is a point in the center that has the maximum upward (upward) displacement from the rest position.
Trough
The trough is exactly the opposite of the crest. The center point that has the maximum downward (negative) displacement from the rest position is called the trough.
Wavelength
The length of a complete wave cycle is called wavelength of a wave. When a pattern repeats itself, it is called a wave. The pattern repeats itself regularly and periodically in space and time. It is determined from the distance from crest to crest or from trough to trough.
Amplitude
When the particle has a maximum displacement from the rest position, it is called the amplitude of the wave. The distance from the resting point to the peak or crest is the amplitude. The amplitude can be determined from the resting position to the trough position. It can also be determined as the distance of the line segment normal to the rest position and moving vertically upward from the rest position to point A.
Transverse Wave Example
There are many longitudinal waves examples from which some are given here.
Earthquake
When there are movements in the earth’s crust because of tectonic plates, the resulting waves are called seismic waves. These waves create a rolling effect as they travel across the Earth’s surface, causing destruction depending on their strength or magnitude.
Electromagnetic waves
Electromagnetic waves also are referred to as EM waves. Electromagnetic radiation is made up of electromagnetic waves which are produced while an electric field comes in contact with a magnetic field. It also can be stated as the electromagnetic waves are the composition of oscillating electric fields and magnetic fields.
Characteristics of Transverse Waves
- The transverse wave can only be passed through solids and cannot pass through liquids or gases.
- Polarization is a phenomenon which can only be observed with transverse waves. In the oscillation plane, also called polarization, all particles in a medium oscillate in the same place.
- When the transverse waves propagate in a medium, the pressure and density will remain constant.
- With transverse waves, the formation of typical wave crests and wave troughs is a natural process.
Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
- Transverse wave is defined as a wave in which the particles of the medium move in the direction perpendicular to the wave.
And longitudinal waves are defined as the waves in which the displacement of the medium is in the same direction of the movement of the wave.
2. The movement of the transverse wave is in the direction of the propagation of the wave.
But the movement of longitudinal waves is in the direction normal to the propagation of waves.
3. Traverse waves contain troughs and crests.
But longitudinal waves contain refractions and compression.
Conclusion
A wave is the movement that occurs in a medium from one point to another when a body comes in contact with it.
There are two types of waves which are Transverse and Longitudinal Waves.
Transverse wave is defined as a wave in which the particles of the medium moving in the direction perpendicular to the wave are longitudinal waves.
A wave consisting of a vibration or periodic disturbance occurring in the same direction as the wave motion.
The velocity of transverse wave is given by
There are many examples of transverse waves such as electromagnetic waves, ocean waves, etc.
Traverse waves contain trough and crest.
The movement of transverse wave is in the direction of the propagation of the wave.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out