A transducer and a sensor are fundamentally different in that a transducer detects quality in one form and alters it to another, whereas a sensor observes fluctuations or adjustments in the environment and outputs the internal format. Identifying the Difference between a Transducer and a Sensor
Transducer and sensor
A transducer is an electrical device that converts energy from one form to another. Microphones, loudspeakers, thermometers, position and pressure sensors, and antennas are all examples of common electronic components. Despite the fact that photocells, LEDs (light-emitting diodes), and even ordinary light bulbs are not typically thought of as transducers, they are all transducers.
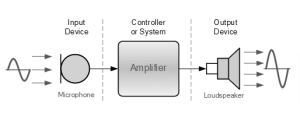
Sensor
It is described as a component that generates a signal that is related to the quantity being measured. The output is often an electrical amount, whereas the measure is a physical quantity, property, or condition that is to be measured.’ The quantity being monitored in the case of, say, a variable inductance displacement element is displacement, and the sensor converts a displacement input into a change in inductance.
Importance of Transducer
Physical forces such as temperature and pressure are difficult to calculate precisely. If these physical forces are converted into an electronic signal, however, their levels may be easily detected with a meter. The primary function of transducers is to convert physical forces into electrical signals that can be easily handled and transmitted for measurement.
The output of the transducer is always in electrical form, proportional to the measured quantity applied to the device. The force is measured using strain gauges in a Wheatstone bridge configuration. Strain gauges measure electrical resistance fluctuations in response to applied force. The signal from the strain gauge goes through signal conditioning, or amplification, before being released as an electrical signal to a Data Acquisition system.
There are two types of transducer
Active Transducer
Passive Transducer
Active Transducer – Active transducers are transducers that do not require a power supply. They work with the idea of energy conversion. They produce a proportionate electrical signal to the input voltage (physical quantity). An active transducer is something like a thermocouple.
Passive Transducer -A passive transducer is one that operates without the use of an external power source. They produce an output signal in the form of a change in resistance, capacitance, or any other electrical property, which must subsequently be translated into an equivalent current or voltage signal. For example, a photocell (LDR) is a passive transducer that changes resistance when light shines on it. This change in resistance is converted to a proportionate signal with the help of a bridge circuit. As a result, a photocell may be used to measure the intensity of light.
Difference Between Transducer and a Sensor
Transducer | sensor |
1.The transducer is a device that, when activated, transforms energy from one form to another. | 1. Physical changes in the environment are detected and converted into a readable amount. |
2. Conditioning of signals and sensors | 2. only sensor |
3. Conversion of energy from one form to another. | 3. Changes are detected, and the necessary electrical impulses are generated. |
4. Other electronic components include the thermistor, potentiometer, thermocouple, and others. | 4. Sensors include proximity sensors, magnetic sensors, accelerometer sensors, light sensors, and so on. |
5. A transducer is a more complex device that transforms a physical quantity into a different output signal (voltage, current). | 5. Sensors include proximity sensors, magnetic sensors, accelerometer sensors, light sensors, and so on. |
Application of a transducer
Transducers in motion-control applications include rotary or linear encoders for position feedback, sensors like tachometers for speed sensing, and even proximity switches to start or stop a machine movement. Pressure transducers, for example, are an important feature of hydraulic motion control systems.
A transducer measures the load on the engines.
They’re employed, which is a technique for detecting muscle action. Transducers are also used in ultrasound machines. The transducers of a speaker transform electrical impulses into acoustic sound. A transducer in the antenna converts electromagnetic waves to electrical impulses. In Robotics & automation, it translates movement into an electrical signal. Nuclear radiation is monitored in a Direct Reading Dosimeter by a transducer that turns the radiation energy into an electrical signal (DRD).Thermocouples and RTDs are utilised in businesses to monitor and adjust system temperature .A photovoltaic cell is a type of transducer that converts sunlight into electrical energy.
Application of a sensor
The sensor is a device which measures physical attributes from equipment, appliances, machines, and other systems, such as temperature, pressure, distance, speed, torque, acceleration, and so on. Using numerous technologies, the sensor generates an electrical/optical signal proportionate to the inputs. These signals are either evaluated or sent on to the next stage for further processing. Long and digital sensors are the two types of sensors. Digital sensors measure the status of physical variables, whereas analogue sensors measure the exact value of physical variables. Sensors, the property perceived, the technology used, and the systems in which they are implemented are all classified as applications. Let’s take a closer look at sensor applications.
Sensors are utilised to manage the level of pressure in oxygen sources, flush the infrared toilet lights, and monitor the patients. Transducers are used to operate engines, monitor HVAC systems, navigate vehicles, and lift or position bridges and ramps, among other things.
Sensors include the likes of thermometers, mercury thermometers, motion sensors, and pressure switches, whereas transducers include the likes of wire extension, microphones, and linear pressure devices.
Conclusion
A transducer is an electrical device that converts energy from one form to another. Active transducers are transducers that do not require a power supply. They work with the idea of energy conversion -A passive transducer is one that operates without the use of an external power source. The sensor is a device which measures physical attributes from equipment, appliances, machines, and other systems, such as temperature, pressure, distance, speed, torque, acceleration, and so on
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






