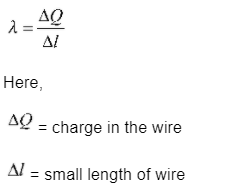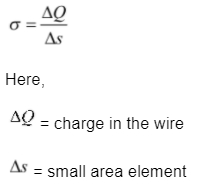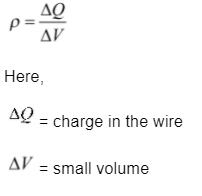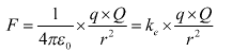The superposition principle allows us to determine the total force on a given charge due to any number of point charges acting on it. Each charged particle in the space around or surrounding it creates an electric field in the universe. The electric field produced by the charge is independent of the presence or absence of other charges. The generated electric field can be determined using Coulomb’s law. Two or more electric fields can be combined by using the superposition principle.
Electric Charges
Electric charge, also known as charge or electrostatic charge, is defined as the fundamental property of subatomic particles which causes them to experience a force when they are placed in an electromagnetic field. Generally, there are two types of electrical charges: positive charges, carried by protons and negative charges carried by electrons. If the net/total charge on an object is zero, that is neither positive nor negative, then it is said to be neutral. Electric charge is represented as Q and measured in coulombs. The unit of charge is the coulomb.
Superposition Principle
According to the principle of superposition, every charge in space produces an electric field at some point, which is independent from the presence of other charges in that medium. The resulting electric field is the vector sum of the electric field due to the individual charges.
Principle of Superposition in Electrostatics
Let us consider, one positive charge and two negative charges which exert force on positive charge. Now, from the superposition theorem, the resulting force is the vector sum of all the remaining forces acting on the body.
Therefore,

Continuous Charge Distribution
In addition to the superposition principle in electrostatics, we have to get an idea of the charge distribution. We know that we get either positive charge or negative charge. The charged element released is called a proton. When these protons are quantized, it is clear that the distance between them is much smaller and they are very tightly bound. So, the charge distribution on them can be given by the principle of superposition.
There are three types of continuous charge distribution which are as follows;
- Linear Charge Distribution
- Surface Charge Distribution
- Volume Charge Distribution
Linear Charge Distribution
If the charges are equally dispersed along a length, for example about the circumference of a circle or along a straight cable or wire, then this is known as a linear charge distribution. it is represented as .
Linear charge density of a wire is determined as
Surface Charge Distribution
The surface charge density is little practical to characterize the charge distribution on the surface of a conductor which is charged with respect to the positions of the small charged elements.
The surface charge density is more practical for an area element S on the surface of conductor (small enough on a macroscopic scale but large enough to carry many electrons) and define the charge Q on that element.
Surface charge density is given as
The surface charge density ignores charge quantization and charge distribution discontinuities at microscopic level, which is a smoothed average of the microscopic charge density over an element of area ∆S, which is very large in microscopic.
Volume Charge Distribution
When charge is distributed over the volume equally then it is known as volume charge density.
Volume charge density is given as
Coulomb’s Law of Electrostatics
Coulomb’s law of electrostatics provides an equation for the electric force between the electric charges.
According to Coulomb’s law of electrostatics electrostatic force between two point charges separated by a distance is proportional to the product of the magnitude of charges and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between these two charges.
The Coulomb’s law is given as
Here,
q = Test charge
Q = Source charge
F = force
r = distance between charges
Conclusion
The superposition principle allows us to determine the total force on a given charge due to any number of point charges acting on it.
According to superposition principle,
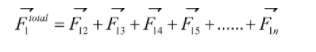
There are three types of continuous charge distribution which are as follows;
- Linear Charge Distribution
- Surface Charge Distribution
- Volume Charge Distribution
Linear charge density of a wire is determined as
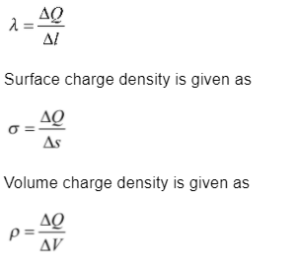
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out