Suppose two sine waves of equal amplitude and frequency propagate on along string in opposite directions .The equation of the two waves are given by

Be a part of Last Mile Program for JEE 2024
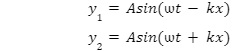
Where, A is amplitude, k is wave number, ω is angular frequency (ω = 2πf, f is frequency)
These waves interfere to produce what we call standing waves.
The resultant displacement of the particles of the string are given by the principle of superposition as
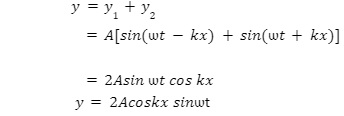
Stationary waves are characterised by nodes and antinodes.
Nodes are the points of the medium which are permanently at rest, i.e. amplitude = 0. The pressure and density variations at nodes are maximum.
Antinodes are the points of the medium at which amplitude of vibration of particles is maximum.The pressure and density variations are minimum at antinodes. Distance between two consecutive nodes and two consecutive antinodes is λ/2. Distance between a node and adjoining antinode is λ/4.
Mode is the name given to any musical sound. The mode of minimum frequency is called fundamental mode or tone or key mode. The simplest mode of vibration (producing fundamental note ) is called fundamental mode. The sounds whose frequencies are greater than the fundamental note are called overtones. When the frequencies of overtones are integral multiples of the fundamental note ,they are known as the harmonics.
Vibrations of stretched strings
Transverse stationary waves are formed on stretched strings. Nodes are formed at the rigid ends , where wedges are held under the string. Antinodes are formed in between, over the stretched string. In any mode of vibration the number of antinodes is one less than the number of nodes.

The frequency of first overtone or second harmonic is n2 = 2n1
Similarly , the frequency of the second overtone or third harmonic is n3 =3 n1 and so on.
Organ Pipes
A pipe filled with air having rigid walls and diameter less than its length is called an organ pipe. Such pipes are used in producing musical sound by pushing air into the pipe. Flute is the best example of an organ pipe. When the pipe is open at both the ends ,it is called an open organ pipe. When one end of the pipe is open and the other is closed , it is called a closed organ pipe.
In an open organ pipe , frequency of fundamental note or first harmonic is

End correction : In organ pipes ,an antinode is not formed exactly at the open end. Rather, the antinode is formed a little distance (x) away from the open end outside it. This (x) is known as the end correction. Its value depends upon the internal radius (r )of the pipe. Usually x = 0.6r
Note that in an open organ pipe, end correction is 2x for the two open ends of the pipe. In a closed organ pipe, end correction is x as there is only for one open end.

Conclusion
Standing wave or stationary wave is the superposition of two waves travelling in opposite directions, each having the same amplitude and frequency . The stationary waves are characterised by nodes (amplitude is 0) and antinodes (amplitude is maximum). Organ pipe is hollow type pipe in which pipes are used in producing musical sound by pushing air into the pipe.
Important Links
| JEE Advanced | Zinc Carbon Cell |
| JEE Notification | Focal length of a convex lens |
| JEE Eligibility | pH scale |
| JEE Syllabus | Probability density |
| JEE Exam Pattern | Equations of a parabola |
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






