Iso stands for constant and thermal stands for temperature. Isothermal processes are the processes in which the temperature is constant. Compression is the process in which the volume of the system is decreased or the pressure is increased. Isothermal compression is the process of compression in which the temperature is constant. It is a thermodynamic process that occurs in a closed system. The process maintains thermal equilibrium.
What is thermal equilibrium?
Thermal equilibrium is the state at which the temperature is constant throughout the system. Two objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium when their temperature is the same.
For example, objects A and B have a uniform temperature of 20-degree celsius. The objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Similarly, the system with a uniform temperature of 20-degree celsius is also in thermal equilibrium.
Equation of ideal gas
Ideal gas is a theoretical gas consisting of particles or molecules which repel each other. Ideal gas molecules can expand in the whole space provided to them. The volume of the molecules or particles is assumed to be zero. Ideal gas follows the ideal gas equation which can be represented as,
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, n is the number of moles, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature of the gas.
Equation of isothermal compression for an ideal gas
As discussed earlier, an ideal gas follows the equation PV = nRT. Now, for an isothermal compression process, the temperature of the system is constant. Assume a closed system, the number of moles, n, will also be constant.
So, the equation of isothermal compression can be written as
PV = C
Where C is the constant.
The above equation can also be written as
T = Constant
T = 0
Assume a system under isothermal compression. Let the initial state is represented as 1 and the final state is represented as 2.
The equation of this system can be written as
P1V1=P2V2= Constant
Graph of the isothermal compression process
P-V curve of the isothermal compression process between states 1 and 2 can be represented as:
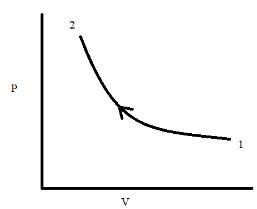
Following things can be observed from the above curve:
- The Process follows the path 1-2.
- The pressure at state 2 is more than the pressure at state 1.
- The volume of the system is decreased from state 1 to 2.
Work done by an isothermal process
The work done by an isothermal process is the integration of dW where dW is the displacement work or PdV.
In this process, the gas follows Boyle’s law (ideal gas), and work done by the gas is
W = nRT ln (Vf / Vi)
where Vf < Vi (compression takes place) and W is negative. f stands for final state and i stands for initial state.
This is also the quantity of heat transferred when the gas volume is changed from Vi to Vf . The molar heat capacity of the system in such a process is infinite because the temperature difference is zero.
Isothermal compression examples
Any compression which has a constant temperature or zero temperature difference is the isothermal compression process. These processes are very slow, as the system needs time to maintain a constant temperature. For example, heating a jar filled with water with a sliding lid. The losses are ignored here as the ideal isothermal compression process is impossible to achieve.
The pressure volume curve of an isothermal compression process can be represented as

The above two curves represent the isothermal process where the temperature is constant and the pressure is increasing or the volume is decreasing. The work done is taken to be negative here as the system needs to work for the process of compression. The work done by a system is a positive quantity as it is a convention and vice versa.
Conclusion
Isothermal compression is the thermodynamic process of decreasing the volume or increasing the pressure when the temperature of the system is constant. The process maintains the state of thermal equilibrium. We have learned about the thermodynamic systems, types of thermodynamic processes, and the details about isothermal compression processes. The work done in an isothermal compression process is also discussed which is a negative work as it is supplied from the external.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






