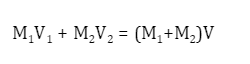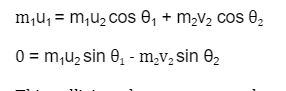When the maximum kinetic energy of colliding objects/systems is lost, an inelastic collision occurs in physics. In a perfectly inelastic collision, the colliding particles stick together. In these cases, the kinetic energy lost is used to join the two bodies. The conservation of momentum and energy is commonly used to solve collision problems.
What is the definition of a collision?
A collision occurs when two or more objects collide and exert forces on each other for a brief period. It is divided into two categories:
- Inelastic Collision
- Elastic Collision
We will discuss inelastic collisions, perfectly inelastic collisions, their formula, and inelastic collision in two dimensions in this article. Let’s take a look at each one individually. Take a look around.
What is the definition of an inelastic collision?
A collision in which kinetic energy is lost is known as an inelastic collision. The system’s momentum is conserved in an inelastic collision, but the kinetic energy is not. This is due to the transfer of some kinetic energy to something else. The culprits are most likely thermal energy, sound energy, and material deformation.
Assume two similar trolleys are approaching each other. They collide, but because the trolleys are equipped with magnetic couplers, they join together and become one connected mass due to the collision. Because the maximum amount of kinetic energy has been lost, this type of collision is perfectly inelastic. This does not necessarily imply that the final kinetic energy is zero; momentum must be conserved.
Examples of Inelastic Collisions
The majority of collisions we see in our daily lives are inelastic collisions. The following is a list of some of them.
Inelastic Collision Examples in the Real World
- The ball is thrown from a certain height and cannot return to its original position.
- When a soft mud ball is thrown against a wall, it sticks to the wall.
- A two-vehicle accident
- A car hitting a tree
Perfectly inelastic Collision
A perfectly inelastic collision is a special case of inelastic collision. When two objects collide, they stick together. For instance, when a wet mud ball is thrown against a wall, it sticks to the wall.
Are there any examples of collisions that are perfectly inelastic?
The ballistic pendulum is a valuable device that creates an inelastic collision. The ballistic pendulum was widely used to measure the speed of projectiles until the advent of modern instrumentation.
A projectile is fired into a suspended heavy wooden block in this device. Initially, the wooden block is stationary. The projectile becomes embedded in the block after colliding with it. Some kinetic energy is converted to heat and sound and then used to deform the block. Momentum, on the other hand, must be preserved.
As a result, the block swings away quickly. The block behaves like a pendulum following the collision, conserving total mechanical energy. As a result, we can use the maximum height of the swing to calculate the block’s kinetic energy after the collision and then use conservation of momentum to calculate the projectile’s initial speed.
Inelastic Collision Formula
To calculate the velocity and mass of an inelastic collision, the inelastic collision formula is used. The final velocity with which two objects move when they collide under inelastic conditions is given by:
Where,
- V is the final velocity.
- M1 is the mass of the first object in kilograms, and M2 is the mass of the second object in kilograms.
- V1 (m/s) is the initial velocity of the first object.
- V2 (m/s) is the initial velocity of the second object.
How do you calculate the velocity of an inelastic collision?
Example:
The moving object has a mass of 4 kg with an initial velocity of 5 ms-1 and the stationary object has a mass of 5 kg. Then find the initial velocity of a moving object?
Given:
Mass of Stationary Object (m1) = 5 kg
Mass of Moving Object (m2) = 4 kg
Velocity of Moving Object (v1) = 5 ms-1
Solution:
Substitute the given values in this formula
Inelastic Collision in Two Dimensions
In an inelastic collision in two-dimension, momentum conservation is applied separately along each axis. Because momentum is a vector equation, each dimension has only one conservation of momentum equation. In the same way, there is only one energy conservation equation.
When an object having mass m1 collides with another object having mass m2 that is stationary, they both move in opposite directions. In addition, the linear momentum of these two masses is conserved in their two-dimensional interaction. The components along the x and y axes will now have the following equations:
This collision phenomenon can be seen while playing carrom, billiards, etc.
Inelastic Collision Kinetic Energy
The kinetic energy is not conserved in an inelastic collision. Internal friction causes kinetic energy to be lost. It may transform into atomic vibrational energy, causing a heating effect and deformation of the bodies.
Let’s solve a problem:
A man is driving a car of mass 300 kg and moving eastwards at a speed of 20m/s. He hit another car of mass 400kg, which stopped at the stop signal. After collision both cars stick together. What is the final speed of the cars?
Solution:
Given,
Mass of car 1 is M1 =300kg
Mass of car 2 is M2 = 400kg
Speed of car 1 is V1 =20m/s
Speed of car 2 is V2 = 0m/s
According to the conservation of momentum , momentum before collision and after collision has same value. Pi = Pf

Thus, after the collision, both cars will move with a speed of 8.57 m/s.
Conclusion
In an inelastic collision, kinetic energy is not conserved. Now you must have a basic understanding of inelastic collisions, including formulas, terms, examples, and applications. We hope that this article has helped you solve all of your inelastic collision problems.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out