Hess’s law of heat summation, or simply Hess’s law, is named after a Russian physician and chemist Germain Hess who published the law in 1840.
Hess’s law is based on the first law of thermodynamics which says that the enthalpy of chemical processes is not dependent on the steps, processes, or ways used in the beginning stage to the final stage. The real need of Hess’s law is to simplify and categorise the chemical reactions individually and analyse the overall energy requirement.
There are two forms of Hess law such as multi-step reaction and multi-different reaction.
Description of Hess’s law
Hess’s law is based on the first law of thermodynamics. It states that the enthalpy of a chemical reaction’s initial and final steps are independent. The formula of Hess’s law:

Enthalpy means the quantity of heat required by the system or expelled by the system to cause a change in the system.
H = P + EV
The first law of thermodynamics defines that the total energy of the product should be the same before and after chemical or physical reactions. Suppose there is a difference in the energy of the product and reactants. In that case, the temperature is fixed or adjusted to equalise and stabilise sum energy. The mathematical expression of exothermic and endothermic reactions is written as:
Exothermic – A + B —–> C + D + △H
Endothermic – A + B +△H—–> C + D
By applying the concept of Hess’s law, we can calculate the hat of allotropic modification, the heat of formation, and other various reactions. Enthalpy can be calculated using different steps throughout the reaction, such as:
- The sign of △H can change place in order to change the result.
- The value of △H must be multiplied by the constant if the constant is used as the sign of multiply in the reaction.
- These two rules stated above can be used in the reaction.
These steps are basic steps of performing the reaction of enthalpy of Hess’s law of heat summation. Other than enthalpy, the Gibbs energy and entropy can be calculated with the help of Hess’s law.
What are the forms of Hess’s law?
The forms of Hess’s law are multi-different reactions and multi-step reactions. Forms of Hess’s laws are defined with their mathematical operations.
Multi-different reaction
By changing the sum of enthalpy chemical reaction, enthalpy of required reaction to the product can be achieved similar to the case of changing the products and reactants of needed chemicals can be achieved by amalgamating several chemical reactions.
Combustion of carbon disulphide, carbon and sulphur is exothermic with the enthalpy of -296.8kJ, -393.5kJ and 1075kJ. The reactions are written as:

These enthalpy changes and reactions can be treated even without performing the experiments.
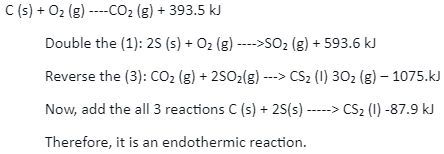
Multi-step reaction
In this form, the reactants tend to make the product by following different steps and using numerous products. The total of all products and reactants and energy changes of products results in an overall change in the reaction.
The product B can be formed using intermediates C, D and E by using different steps. According to Hess’s law, the value of enthalpy △H will be the same regardless of the way crossed.

As the value of both sides will be equal, the energy will not change whether we use a different path or a single-step path for reaction.
Importance of Hess’s law
Atoms to molecules have their own energy. Hess’s law simplifies identifying the layers of steps following in the energy determination. The level of energy may vary from one reactant to another. The process of forming and separating bonds includes energy. The forms of Hess’s law play a significant role in calculating the enthalpy of heat.
Conclusion
This article explains Hess’ law. Hess’s law is based on the first law of thermodynamics which says that the enthalpy of chemical processes is not dependent on the steps, processes, or ways used in the beginning stage to the final stage. Hess’s law helps measure the energy required in the reaction between reactants and products. It also manages the energy level and keeps it equal for uniform experimentation.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






