Every atom has a charge; an atom is said to be charged if it has an uneven quantity of electrons and protons; an atom is said to be positively charged if it has fewer electrons than protons; and negatively charged if it has more electrons than protons.
The bodies are charged in a variety of ways, the most common of which is rubbing. When you rub a plastic comb through your hair, it picks up electrons; but, if we get little bits of paper next to the comb, it draws them like a magnet attracts iron filings, because the electrons attract the positive charge on the paper. This is the charge’s force.
Force between charges
When you touch a plastic comb or a plastic scale against your hair and then bring them close to small bits of paper, the plastic body acts like a magnet, attracting the paper to itself.
Because the plastic body gains electrons from your hair when it rubs against it, it has a stronger negative electric charge. Negative charges attract positive charges already existing in the microscopic pieces of paper, causing them to adhere to the plastic body. The force of charges acting on them causes the attraction or repulsion of differentially charged things.
There are the rules that help to find the force between multiple charges. They are:
- Coulomb’s law
- Principle of superposition
Law of coulomb
“Force between two-point charges varied inversely as the square of the distance between the charges, was directly proportional to the product of the size of the two charges, and acted along the line connecting the two charges,” according to Coulomb’s law. The formula for force, according to the statement, is:
F=kq1q2r2
Where,
Depending on the charges, F is the magnitude of the attraction or repulsion force.
The Coulomb’s constant is k. The value of k in SI units is 9109
The magnitudes of two charges are q1 and q2.
The distance between two charges is denoted by r.
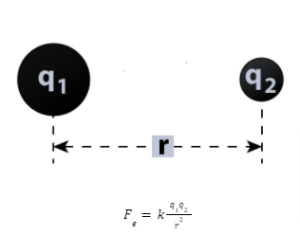
Fe=kq1q2r2
Coulomb calculated the amount of the electric force by using a torsion balance to measure the force between charged objects (a torsion balance is a device that measures gravitational acceleration on the Earth’s surface). This force was thus experimentally shown between two static charged particles. Anything that does not move or change through time is referred to as static.
As a result, k is abbreviated as k =14π0The modified Coulomb’s formula is spelled out as follows:
F=14π0q1q2r2
Where,
The permittivity of free space (or, to put it another way, the ability of a material/ medium to permit or transmit an electric field) is 0.
The Superposition Principle
The force on any charge due to a number of other charges is the vector sum of all the forces on that charge due to the other charges, taken one at a time, as experimentally proven. Due to the presence of other charges, the separate forces remain unaffected. This is known as the superposition principle.
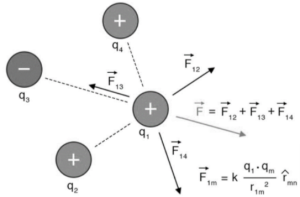
Because force is a vector quantity, it is critical to consider the direction when formulating the formula when there are forces acting from several charges. Consider the following three-point sources in a vacuum: q1, q2, and q3. We must sum the forces acting on q1 from q2 and q3 to get the total force acting on q1. For the force exerted on q1 by q2:
F12 =140 q1q2r12×r12 r12
And then we find the force between the charges q1 and q3 as:
F13 =140 q1q3r13×r13 r13
Then the total on the charge q1 is the sum of these forces.
F=F12 +F13
According to the declaration of the principle of superposition, the force exerted by q1on q2will be the same as Coulomb’s law, and this force will be unaffected by the presence of other point sources such as q3, q4…. qn. As a result, we should add the vector sum of all the forces – to calculate the overall force ‘F’ experienced by q1. The vector sum of all the products is calculated using the parallelogram law of vector addition. We can see that understanding the forces acting from numerous charged sources on a single charged spot requires a combination of both Coulomb’s equation and the idea of superposition.
Newton’s third law accords with Coulomb’s law
The force felt by a charged particle is proportional to the magnitude of the other charged source and inversely proportional to the distance between the two charged point sources’ centres.
When there are many charged point sources, the force on a single point source adds up since each point source’s force works on one charged point independently.
The polarity of a charge is indicated by its sign, not its strength. Its strength is determined by its magnitude. To understand the attraction or repulsion between charges, the positive or negative sign is utilised.
Conclusion
The bodies are charged in a variety of ways, the most common of which is rubbing. When you rub a plastic comb through your hair, it picks up electrons. When you touch a plastic comb or a plastic scale against your hair and then bring them close to small bits of paper, the plastic body acts like a magnet, attracting the paper to itself. When there are multiple charges, according to Coulomb’s law, the force is always exerted in a straight line or radially from the two centres of the point source.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






