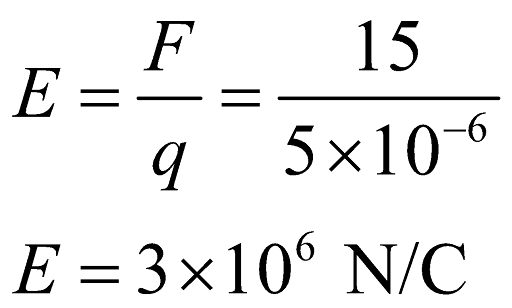Electrostatics is a branch of physics which is concerned with the study of electromagnetic phenomena in which electric charges are at rest, that is when there are no moving charges after static equilibrium is established. In physics, the electrostatic phenomenon refers to the properties of slow-moving or static electrical charges.
The study of stationary electrical charges is called electrostatics. The charge associated with matter, due to which it produces and experiences magnetic and electrical effects, is called electric charge. When you rub a plastic stick with fur or a glass stick with silk, pieces of paper are attracted, which means both sticks are electrically charged.
Electric Charges
Electric charge, also known as charge or electrostatic charge, is defined as the fundamental property of subatomic particles which causes them to experience a force when they are placed in an electromagnetic field. Generally, there are two types of electrical charges: positive charges, carried by protons and negative charges, carried by electrons. If the net/total charge on an object is zero, that is neither positive nor negative, then it is said to be neutral. Electric charge is represented as Q and measured in coulombs. The unit of charge is the coulomb.
Positively Charged Particles
In the case of positively charged particles, the number of positive ions is greater than the number of negative ions. In other words, the number of protons is greater than the number of electrons.
To make the positively charged particles neutral, electrons from the surroundings come to that particle until the number of protons and electrons are equal.
Negatively Charged Particles
In case of negatively charged particles, the number of negative ions is greater than the number of positive ions. In other words, the number of electrons is greater than the number of protons.
To neutralize negatively charged particles, as the protons cannot move and cannot reach the negatively charged particles, the electrons move towards another particle around them.
Neutral Particles
Neutral particles involve an equal number of protons and electrons. Neutral particles have all protons, neutrons and electrons but the number of positive ions (protons) are equal to the number of negative ions (electrons).
Conductors
Conductors are the materials or substances which allow current to flow through them. In addition, conductors allow heat to be transferred through them.
Insulators
Insulators do not allow electrons to flow. The electron bonds in insulators are tighter than in conductors, so they cannot move easily. Glass, rubber, plastic, wood and air are some examples of insulators.
Atoms with the same charge repel each other and atoms with opposite charges attract each other.
Coulomb’s Law of Electrostatics
Coulomb’s law of electrostatics provides an equation for the electric force between the electric charges.
According to Coulomb’s law of electrostatics, electrostatic force between two-point charges separated by a distance is proportional to the product of the magnitude of charges and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between these two charges.
The Coulomb’s law is given as
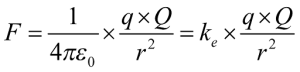
Here,
q = Test charge
Q = Source charge
F = force
r = distance between charges
Electric/electrostatic field is produced by the electric charge or can be produced by time-varying magnetic fields.
Electrostatic Force
The electrostatic force is defined as an attractive and repulsive force between particles which occurs to their electric charges. Electric force between static charged bodies is called the electrostatic force. It is also termed as Coulomb’s force.
Electrostatic force is the fundamental force. There are four fundamental forces in the universe, which are
- Strong nuclear force,
- Electromagnetic force
- Weak nuclear force
- Gravitational force.
The electrostatic force is below the electromagnetic force. Electrostatic force exists between two charges which are placed at a distance. The magnitude of the electrostatic force depends on the magnitude of charges and the distance between them.
Electrostatic Field
Electrostatic fields bear a certain resemblance to magnetic fields. Objects attract each other when their charges have opposite polarity (+/-) and Objects repel each other when their charges have the same polarity (+/+ or -/-). Electrostatic flux lines near two oppositely charged objects are similar to magnetic flux lines between and around a pair of opposite magnetic poles. The electrostatic and magnetic fields are different. Electrostatic fields are checked/blocked by metallic objects, while magnetic fields can penetrate most (but not all) metals. Electrostatic fields arise from a voltage gradient or potential difference and can exist when charge carriers such as electrons are stationary (hence the “static” in “electrostatic”). Magnetic fields are created by the movement of charge carriers, i.e. current flow.
Conclusion
The study of stationary electrical charges is called electrostatics.
Electric charge, also known as charge or electrostatic charge, is defined as the fundamental property of subatomic particles which causes them to experience a force when they are placed in an electromagnetic field.
In the case of positively charged particles, the number of positive ions is greater than the number of negative ions.
In case of negatively charged particles, the number of negative ions is greater than the number of positive ions.
There are four fundamental forces in the universe, which are
- Strong nuclear force,
- Electromagnetic force
- Weak nuclear force
- Gravitational force.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out