Introduction:
Electric current creates the magnetic field in an electromagnet. A wire looped around a coil is the most common building block of an electromagnet. Electromagnetism occurs when current flows through the wire, creating a magnetic field in the coil’s centre. Electromagnets are made by winding a wire around a soft iron core in a circular loop, basically known as a solenoid. An electric current is passed through the wire to create a magnetic field around it. The strength of the magnetic field totally depends upon the number of loops and the intensity of the electrical current.
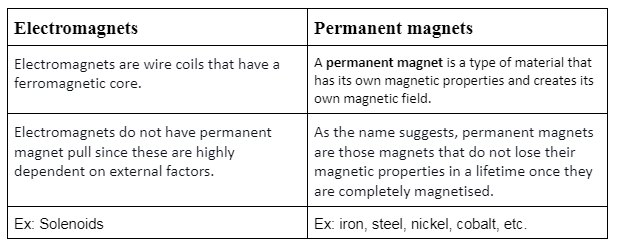
A permanent magnet is a type of material that has its own magnetic properties and creates its own magnetic field. Materials such as iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, etc., are strongly attracted towards a magnet within a certain distance and are hence called ferromagnets. Some of them are naturally occurring ferromagnets, such as loadstones.
Electromagnets
Properties of electromagnets-
The following are some of the magnet’s characteristics:
- The magnetic properties of ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt make them particularly attractive
- When two opposite poles come into contact, they repel each other
- A free-floating magnet’s directive property is that it always points north-south
Working principle of electromagnets-
So, how exactly do they work? Let’s take a closer look at the iron nail. When it is not influenced by an electric field, why does it not generate a magnetic field?
Nails are typically made up of thousands of separate magnetic dipoles, which cancel each other out when atoms in the nail are oriented in random ways. These atoms are reoriented to point in the same direction under the influence of electric current. A powerful magnetic field is created when the combined fields of all these tiny magnets are added together. Reorientation occurs as the current flow rises, resulting in increased magnetic field strength. Increasing the current flow has no effect on the magnetic field generated after all particles have been completely reoriented in the same direction. The magnet is said to be saturated at this stage.
Uses of electromagnets-
Some electromagnet uses are given in the points mentioned below:
- Amplifiers
- MRI machines
- Particle Accelerators
- Magnetic Separation
- Spacecraft Propulsion Systems
- Electric Motors and Generators
- Control Switches in Relays
- Transportation
- Induction Heating
- Hard Drives
Disadvantages of electromagnet-
Electromagnetism has a few drawbacks, such as the following:
- They get really hot very quickly
- It takes a lot of power to run
- They have a magnetic field that can store a lot of energy
- The power goes out if the electricity is cut off
Permanent magnets
Properties of permanent magnets:-
There are some major properties of a permanent magnet that show that a material is a permanent magnet:-
1:- High retentivity:- Magnet should be strong and never lose its attractive property until an external force is applied.
2:- High coercivity:- Its magnetisation should not be affected by extra magnetic fields.
3:- Permanent poles:- A magnet has two poles that are never isolated – that’s why it workes as a compass.
4:- High permeability:- A magnet should always attract a piece of iron and easily magnetise it.
Earlier, we talked about magnetic fields – which is an important property of every magnet – let us now learn about the magnetic field of a permanent magnet.
Types of Permanent magnet:-
These are materials found naturally, and once they are magnetised, they work as a magnet for a long period of time.
There are four types of permanent magnets:-
Neodymium Iron Boron(NdFeB):-
This type of magnet is rarely found on earth and has high coercive force, low mechanical strength, and low corrosion resistance if it is opened. e.g., gold, iron, etc.
Samarium Cobalt (SmCo):-
These are expensive, have low mechanical value, and have temperature resistance – for example, SmCo5, Sm2Co17, etc.
Alnico:-
This magnet is formed from three important materials, and it gets the name Alnico by summarising their names (Aluminium+nickel+cobalt). It has good temperament resistance, is easily demagnetised, and also has other properties like other rare earth materials.
Ceramic or Ferrite:-
These magnets are made from iron oxide, strontium carbonate, and ceramic. They are brittle in nature.
Common uses of permanent magnets:-
1:- Microphone:- It works on the principle of a permanent magnet. When a coil moves from a magnetic field, it produces an electric signal which becomes sound after further processing.
2:- Door locks:- It works with the help of a strong magnet and is often used in commercial or public doors.
3:- Engines or Generators:- These are some of the best applications of magnets, which also use some electromagnetic technology and form electrical energy from mechanical energy and sometimes vice-versa.
Difference between Electromagnets and Permanent Magnets
- Permanent magnets are magnetized permanently and electromagnets are temporary magnets.
- Permanent magnets are made up of hard but the electromagnets are made from soft materials.
- The intensity of magnetic field of permanent magnets are fixed but intensity of magnetic field is adjusted in electromagnets.
Conclusion
Magnetic field and strength are main differences between and electromagnets permanent magnets. A wound coil creates the magnetic field in an electromagnet, while the magnetic field of a permanent magnet (bar) cannot be changed.
Permanent magnets have the ability to maintain their magnetism and magnetic properties over a long period of time.
here are many types of permanent magnets which are
- Alnico magnets.
- Samarium Cobalt Permanent Magnet.
- Neodymium Iron Boron Magnet.
- Flexible Magnet.
The magnetic field that is created by the current flowing through the coil is responsible for electromagnets.
The following important types of electromagnets are given below.
- Resistant electromagnets.
- Superconductor Magnets.
Conclusion:
Electromagnets are wire coils that have a ferromagnetic core. In case the electric current passes through the electromagnets, they start to react like bar magnets. Electromagnets do not have permanent magnet pull since these are highly dependent on external factors. Permanent magnets are those magnets that do not lose their magnetic properties in a lifetime once they are completely magnetised. However, permanent magnets can be demagnetized if placed at extremely high temperatures or by stroking two magnets inappropriately.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






