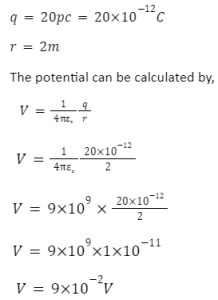The amount of work required to shift a unit charge from a reference point to a specific place in an electric field is known as electric potential. The reference point is usually Earth, but any place outside of the electric field charge’s effect might be utilised. Voltage is another term for electric potential.
The aim is to transport a unit charge (+q) from infinity (somewhere outside the electric field) to a position inside the electric field against the field. The unit charge must do some effort in order to go from infinity to anywhere in the field, or from one point to another in the field, because the electrostatic force created by the electric field is against it.
- Vx is called electric potential at a point x if work is done to transport the charge from infinity to point x.
- Vy is called electric potential at a point y which is the result of work done to transport the charge from infinity to point y.
- The potential difference Vxy between x and y is the name given to the work done to shift the charge from x to y.
Electric Potential Formula
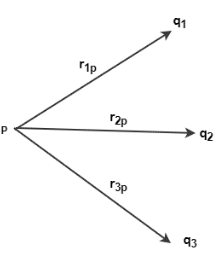
Electric Potential V=Work Done(W)/Unit Charge(q)
V=W/q
V=Joule/Coulomb
As we know that JC-1=V(volt)
Therefore, the S.I. unit of electric potential is Volt(V).
Electric Potential Energy
The total work done by an external agent in transporting a charge or system of charges from infinity to the current configuration without incurring any acceleration is referred to as the electric potential energy of that charge or system of charges.
The entire potential energy a unit charge will have if it is positioned anywhere in space is known as electric potential energy.
Formula for Electric Potential Energy
If two charges q1& q2 separated by distance r,
The formula for electric potential energy is given as:
Electric Potential Due to Point Charge
In the diagram below, a point charge is shown. The equipotential is represented by the concentric circles. This means that the potential is the same at all points on a single surface. The purpose is to compute the electric potential between two points A and B due to this point charge.
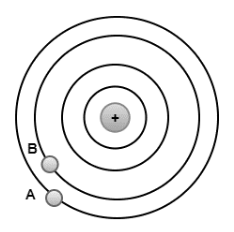
The electric potential difference is also known as voltage, and it is measured in Volts.
![]()
A definition in terms of absolute potential is required because the potential has been defined as a difference. To come up with this new definition, let’s change the above phrasing. The electric field and potential are considered to be zero at infinite. The potential at each location will now be calculated in terms of the infinite, yielding an absolute value for the potential.
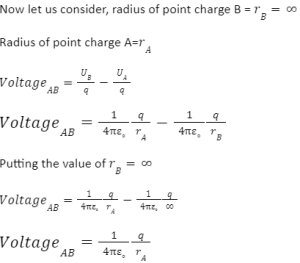
Electric potential due to Multiple Charges
In actual life, you’ll rarely come across a single-point charge. The majority of real-world systems have numerous charges. The total potential at a point in a system of point charges is equal to the algebraic sum of the potential for individual charges at that point. A multiple point charges are depicted in the diagram below.

Some Essential Points related to Electric Potential
- The electric potential is zero at a location halfway between two equal and opposite charges, but the electric field is not.
- If one joule of work is done in pushing one Coulomb of charge against the electric field, the electric potential at that place is said to be one volt.
- When a negative charge is transported from point A to point B, the system’s electric potential rises.
- Infinity is the reference level used to determine electric potential at a place. It denotes that at the reference level, the force on a test charge is zero.
- Since the earth is so massive that adding or subtracting charge from it has no effect on its electrical state, the surface of the earth is assumed to be at zero potential.
Conclusion
The amount of work required to get a unit positive electric charge from infinity to a point in an electric field is defined as electric potential. Similarly, the energy required to transfer a unit positive charge from one position to another is defined as the potential difference between two points.
When a body is charged, it might attract an oppositely charged body while repelling a body that is similarly charged. That is to say, the charged body has the power to work. The electrical potential of a charged body is defined as its ability to conduct work.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out