The dimensions of a physical quantity are the powers to which the basic quantities are elevated to represent that amount. The dimensional formula of any physical quantity is an equation that explains how and which of the base quantities are contained in that amount. It is written by enclosing the symbols representing base amounts in square brackets with the corresponding power, i.e. [].
E.g., the dimension formula of displacement is [L].
In general, the total height of a wave is called its amplitude. According to Physics, Amplitude refers to the maximum dispersion of a point on a vibrating subject from its equilibrium point. As a result, the amplitude of a pendulum is one-half of the distance travelled by the bob as it moves from one side to the other. Vibrating sources produce waves, and their amplitude is proportional to the source’s amplitude.
Intensity
Power in a unit area is called intensity. Its unit is kg.s-³. In the case of light, intensity is defined as the rate at which light spreads over a surface of a given area. Its magnitude generally depends upon the amplitude and wave under propagation. Sound intensity is sometimes known as acoustic intensity.
Mathematically, it is represented by the following formula:
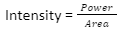
Unit of intensity is watt per square metre.
We can classify intensity into two types: low intensity and high intensity.
Some examples of intensity are the intensity of the kinetic energy carried by drops of water from a sprinkler, the ability to run miles on end at a good speed, and the quickness with which a treadmill is moving.
We know that intensity can be defined as power in a unit area, so we can also define intensity as energy density per unit volume multiplied by the velocity at which the energy is moving. It is measured on the plane perpendicular to the direction of energy propagation.
We can compare the intensity of one sound with another if the frequency of both sounds is the same. If the ratio of power values is 10, then the difference of the sounds is measured as 1 bel.
Dimensional formula of intensity

The intensity of the magnetising field
A part of the magnetic field that arises from the external current rather than the intrinsic properties is magnetic field intensity or magnetic field strength, or magnetic intensity. Also, the magnetic field is the area around the magnet or where the magnetism effect is felt. In a wire that carries current, the formation of magnetic fields takes place. The direction of induced current and the direction of the magnetic field is directly related to each.
In the simplest form, magnetism can be defined as a type of interaction that occurs among the moving charged particles. Spatially separate objects and materials are related to magnetic interactions transmitted by magnetic fields of magnets. A magnetic field is a unique form of electromagnetism.
Conclusion
Intensity is nothing but power in a unit area. We can also define intensity as energy density per unit volume multiplied by the velocity at which the energy is moving. It is measured on the plane perpendicular to the direction of energy propagation. Its unit is kg.s-3. Its magnitude generally depends upon the amplitude and wave under propagation. Some examples of intensity are the kinetic energy carried by drops of water from a sprinkler, the ability to run miles on end at a good speed, and the quickness with which a treadmill is moving.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






