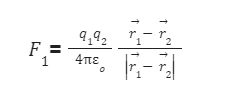By the process of friction or rubbing, conduction and induction a neutral body loses its electron and gets electrified to a charged body. Those two charged bodies influence the surroundings and create an electric field. In the presence of another charge in the electric field of a charge, the field modifies and a special type of attraction or repulsive force is created at that time and this special force is known as electrostatic force.
William Gilbert coined the word electricus. It gives rise to the English words “electric” and “electricity”. In the early of the 18th centuryDaniel, Bernoulli and Alessandro Volta suspected that the electrostatic force diminished with distance as the force in Newton’s law in gravity( as the inverse square of the distance or inverse-square law) which is after proposed by Joseph Priestleyin 1767 that electrical force between charges varied with the inverse square of their distance. In the 1770 s, the dependence of the electrostatic force between charged bodies upon both distance and charge had already been discovered, but not published by Henry Cavendish.
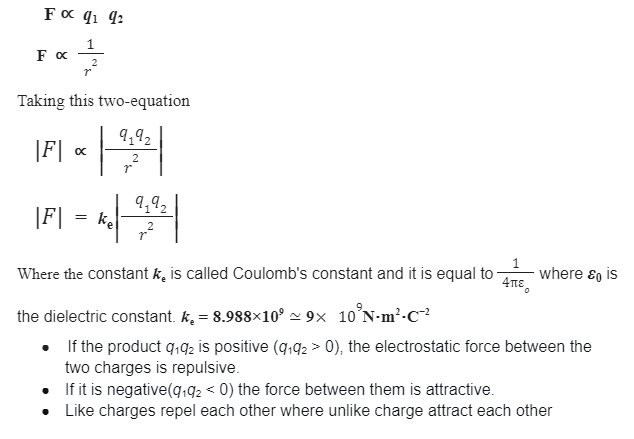
Finally, in the year 1785, the French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb published his first three papers on electricity and magnetism where he stated his law. This publication was very very essential to the development of the electromagnetism theory. He used a device named torsion balance to study the repulsive and attractive forces of charge body, and estimate that “The magnitude of the electric force like repulsive or attractive between two-point charge is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them”.
SCALAR FORM OF THE LAW
This law can be stated as in a simple mathematical expression. The scalar form of this law gives the magnitude of the electrostatic force.
If F is the force between two point charges q1 and q2, and r is the distance between the charges, then according to coulomb’s law
DIELECTRIC CONSTANT
Dielectric is a substance that has a tendency or ability to store electric charges and the ratio of permeability of medium to the permeability of free space is known as dielectric constant.

Vector form of Coulomb’s law
Force has both magnitude and direction and therefore is a vector quantity. Coulomb’s law can be written in the form of a vector. The electrostatic force F1 experienced by a charge q1 at position vector r1 on another charge q2 at positionvector r2 in space is equal to,
Some important points regarding the law
- The law obeys Newton’s 3rd law.
- This law depends on the medium where the charge is present.
- It is a central force meaning it acts along the line between the two charges.
- It obeys the inverse square law.
- Coulomb’s force is extraordinarily strong compared to the gravitational force. However, unlike gravitational force, it cancels since it can either attract or repulse.
Limitations of Coulomb’s law
Certain conditions govern Coulomb’s law and cannot be used freely like most other formulas. These conditions are:
- We can use the formula if the charges must be static or stationary to each other.
- The charge must have a point charge. ( spherically symmetric).
- The formula is valid only when the solvent molecules between the particles are considerably larger than both the charges.
- The charge must be a distinct point charge. (they must not overlap)
- The force depends on the medium where the two charges are kept.
Conclusion
Frenchman Charles de Coulomb was the first to publish the mathematical equation that describes the electrostatic force between two objects.Coulomb’s law gives the magnitude of the force between point charges as F= k(q1q2)/r2.This Coulomb force is extremely basic, since most charges are responsible for all electrostatic effects and underlie most macroscopic forces.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out