Heat cannot transfer from a cold system to a hot system on its own without some external activity being done on the system. This is precisely what refrigerators and heat pumps are designed to do. Heat moves from hot to cold in a refrigerator, but only when it is compelled to do so by external work. Refrigerators are powered by electric motors, which necessitate the contribution of their surroundings in order to function.
What is Clausius’s statement?
Clausius showed that when a little quantity of heat q is introduced to a system that is at an absolute temperature T, the system would undergo a process and that the ratio Q/T is the same for all reversible processes, which was previously unknown. He calculated the value Q/T = dS and designated S as the entropy.
Heating from a lower temperature reservoir to one that is hotter is not achievable on its own. To put it another way, heat transfer occurs automatically only when temperatures drop. For example, we can’t design a refrigerator that runs on electricity alone.
Who was Rudolf Clausius?
Rudolf’s full name is Rudolf Julius Emanuel Clausius. He was a German mathematician and physicist who was responsible for the development of thermodynamics and the Clausius assertion. He found a lot of ideas about how heat and properties work, which is a restatement of the Carnot cycle. In the year 1850, he also wrote a paper titled “The Moving Force of Heat.” In 1865, he proposed the idea of entropy, and in 1970, the virial theorem.
Kelvin – Planck statement
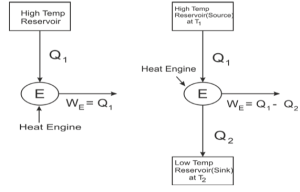
For any given amount of heat, a system cannot provide the same amount of work output as it receives from a high-temperature reservoir. While a system that converts work into heat is possible, a device that converts heat back into work is not viable. Thermal efficiency cannot be 100 percent with a heat engine, on the other hand.
Application of the second law of thermodynamics
Heat is always transferred from a hotter to a cooler body.
Refrigerators and heat pumps are subject to the second law of thermodynamics, which is based solely on the Reversed Carnot cycle. All types of heat engine cycles, such as Otto and diesel, are subject to the second law of thermodynamics.
When we need to chill anything down, we place it in the refrigerator to remove the heat; however, this does not happen automatically. The use of a compressor to deliver external work chills the food, and the same principle is used in air conditioners and heat pumps.
Entropy
The degree of order and disorder, as well as reversibility and irreversibility, are all related to entropy. The entropy notion in thermodynamics is used to assess the degree of difference between irreversible and reversible processes. If a system remains isolated, the entropy of the system continues to rise due to irreversible processes until it reaches the highest likely value once the system enters thermodynamic equilibrium. All irreversible processes come to a halt in the condition of equilibrium. When a system begins to transfer entropy to its surroundings, it is no longer in equilibrium, and irreversible processes occur, resulting in entropy creation. Heat or mass transfer can be used to convey entropy. Because of the entropy generated by irreversible processes within the system, total entropy (system+surroundings) at the exit state is greater than the entropy at the inlet state if there is no entropy accumulation within the system. The term “entropy” refers to a wide range of properties.
The second law of thermodynamics
According to the second law of thermodynamics, when energy is transferred or changed, more and more of it is squandered in the process. In thermodynamics, there are four laws that describe the interactions between thermal energy (heat) and other forms of energy, as well as how energy affects matter. This is one of those laws. The First Law of Thermodynamics asserts that energy cannot be created or destroyed; the total amount of energy available to be used by all things in the universe remains constant. The Second Law of Thermodynamics deals with the nature of energy and how it can be transformed.
Clausius statement diagram
Conclusion
In thermodynamics, there are four laws that describe the interactions between thermal energy (heat) and other forms of energy, as well as how energy affects matter. The First Law of Thermodynamics asserts that energy cannot be created or destroyed; the total amount of energy available to be used by all things remains constant.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






