A two-terminal electronic component that conducts the current(I) in one direction is called a diode. In diodes, the most commonly used diode is a semiconductor diode. In this article, we look at the special type of semiconductor diodes, their internal construction, and their types with the application.
The relationship between the current flowing through the diode and the voltage due to the applied voltage in Photo-Diode is shown. Thus showing the voltage and diode current through the graph is called IV characteristics of the diode.
Photodiode
Photodiodes are a special type of semiconductor diodes that convert light into electrical energy when exposed to light.
The junction of the photodiode is illuminated then the electric current flows through the two terminals.
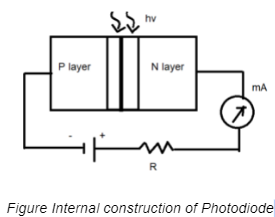
Construction of photodiode
The PN junction of the photodiode is placed inside a glass. This transparent glass allows light to pass through the diode. The other side of the glass is insulated.
Working of photodiode
When the photodiode is not exposed to light or radiation, the electrons in the p side flow through the junction. As the minority carriers flow through the junction, there will be a flow of reverse current. This current is called dark current.
When the photodiode is exposed to light, the temperature of the junction will increase. The electrons and holes will get separated from each other. The electrons in the n side will get attracted towards the positive terminal of the battery, and the holes in the p side will get attracted to the (-) terminal of the battery.
As a result, a high amount of reverse current gets generated through the junction. When the light intensity increases, more carriers are generated and flow through the photodiodes. Hence, a large current is produced.
The light intensity is directly proportional to the electric current.
Forward Bias and Reverse Bias condition
There are two ways in which a p-n junction diode can operate, i.e., forward and reverse bias.
Forward biassing is when the positive terminal of the power supply is connected to the junction’s P region, and the battery’s negative terminal is connected to the N region of the junction.
Reverse biassing is when the positive terminal of the power supply is connected to the junction’s N region, and the battery’s positive terminal is connected to the P region of the junction.
I-V characteristic of photodiode
In the I-V characteristic graph of photodiodes, the x-axis represents the reverse applied voltage, and the y-axis represents the current that flows through the device on the application of reverse voltage.
As we have already discussed in the workings, a small reverse current will flow through the device, and this current is known as dark current (represented on the x-axis).
When the junction is illuminated, the current will increase and become independent of the applied reverse voltage.
Hence the carriers will flow only due to the radiation intensity with the increase in temperature, and the reverse bias condition will not play any role in this situation.
We can clearly say that after illumination, the curve shows equal spacing. That happens because the intensity of the radiation falling on the junction of the photodiode is directly proportional to the current flowing through the device, or we can say that the current increases with the increase in temperature or intensity of light.
Photodiode working operates in reverse bias conditions. Reverse current sometimes gets completely independent of the reverse voltage. In the condition of no illumination, the reverse currents are zero. When the light increases, the reverse current also increases.
Applications of Photodiode
- Photodiodes have numerous applications such as medical equipment, light detectors, smoke, or fire detectors as they are highly responsive to the temperature.
- Solar panels are made by using these photodiodes. These diodes provide electric isolation.
- Camera sensors also contain photodiodes as a camera requires light-sensing ability for best performance.
- They are used in photoconductors and photomultiplier tubes.
- They are used in tomography and many more medical applications.
Conclusion:
The I-V characteristics of a photodiode working and how it works in reverse bias condition is discussed with the working principle of the photodiode and proper explanation, and the concept of forward biasing and reverse biassing.
We studied some of the significant applications of the photodiode and learned about the uses of photodiodes in various sectors such as safety and medical applications.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out