A straight line is an unending figure in one dimension that does not have any breadth to it. It consists of an unending series of points connected together on either side of a point. A straight line does not contain any curves at any point along its length. It may be positioned horizontally, vertically, or at an angle. If we use any two points on the straight line to draw an angle, we will invariably end up with a result equal to 180 degrees. During this brief introduction to the topic, we will investigate the world of straight lines by becoming familiar with the equations of straight lines expressed in a variety of formats and learning how to solve problems that are based on straight lines.
Straight Line
A line is said to be straight if it is of an endless length and does not contain any curves in it. It is also possible to build a straight line between two points, although in this case, both ends of the line will extend to infinity. A straight line is a figure that is formed when two points A (x1, y1) and B (x2, y2) are connected with the shortest distance between them, and the line ends are extended to infinity. This creates a figure known as a straight line.
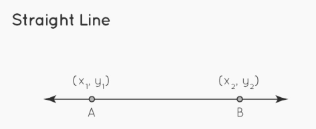
The following illustration shows a line that is perfectly straight when travelling from point A to point B. The letters A and B are used to symbolise the straight line AB.
Types of Straight Lines
There are many distinct varieties of straight lines. In most cases, the alignment of the straight lines is used to categorise the straight lines. The angle that they make with either the x-axis or the y-axis is referred to as their alignment. The following categories can be assigned to them according to the arrangement of the straight lines:
- Horizontal lines
- Vertical lines
- Oblique or Slanted lines
Let us investigate each of them in turn.
Horizontal Lines
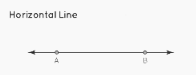
Lines that are drawn horizontally and are either perpendicular to the y-axis or parallel to the x-axis are referred to as horizontal lines. They make an angle with the x-axis of either 0 degrees or 180 degrees, and they make an angle with the y-axis of either 90 degrees or 270 degrees.
In the given figure,
←→
AB
is a horizontal line
Vertical Lines
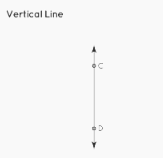
Vertical lines are lines that are drawn vertically and are either parallel to the y-axis or perpendicular to the x-axis. These lines are referred to as vertical lines. They make an angle of 90 degrees or 270 degrees with the x-axis, and they make an angle of 0 degrees or 180 degrees with the y-axis.
The line denoted by CD is depicted as being vertical in the illustration.
Oblique or Slanted Lines
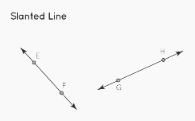
The lines that are drawn in an oblique position or make an angle that is not 0 degrees, 90 degrees, 180 degrees, 270 degrees, or 360 degrees with the horizontal or vertical lines are referred to as slanting lines or oblique lines.
In the illustration, the lines denoted by the symbols EF and GH are inclined.
Characteristics of a Line that is Straight
The characteristics of straight lines are outlined in the following text.
- The length of a straight line can never be measured. We will never be able to accurately determine the distance that separates the line’s two extreme points
- A line that is perfectly straight has no regions and no volumes. despite this, its length is unbounded
- A figure with only one dimension is called a straight line
- It is possible for an endless number of lines to pass through a single point, yet there is only a single line that can be traced that goes through two points
Equation of a Straight Line
A linear equation is an equation that can be represented by a straight line. When placed on a cartesian plane, a straight line can be represented in a number of various ways depending on the variables, angles, and constants that are known. The degree of steepness of a straight line can be inferred from its slope, which also serves to identify the direction in which the line points. The formula for calculating it is the change in y coordinates divided by the difference in x coordinates; this ratio is sometimes referred to as rise over run.
The Equation of a Straight Line in Its Most General Form:
The equation for a straight line can be written as axe + by + c = 0, where axe, by, and c are constants.
- a, b, c are constants, and x, y are variables.
- The slope is -a/b .
Conclusion
A straight line is an unending figure in one dimension that does not have any breadth to it. It consists of an unending series of points connected together on either side of a point. A straight line does not contain any curves at any point along its length. It may be positioned horizontally, vertically, or at an angle. If we use any two points on the straight line to draw an angle, we will invariably end up with a result equal to 180 degrees.There are many distinct varieties of straight lines. In most cases, the alignment of the straight lines is used to categorise the straight lines. The angle that they make with either the x-axis or the y-axis is referred to as their alignment.The length of a straight line can never be measured. We will never be able to accurately determine the distance that separates the line’s two extreme points.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






