In mathematics, a locus is a collection of points that satisfy a specific criterion or scenario for a shape or structure. The locus is pluralized as loci. From the word location comes the term locus. A locus is a curve or a form. Any shape or curve, we know, is created by a set of points. As a result, “Locus” is a collection of points.
Geometric patterns were once thought of as an object or a location where points might be found or moved before the twentieth century. Modern mathematics, on the other hand, recognises entities as a set of points that satisfy a specific condition. The region is the area where the loci are located. We will learn about locus meaning in arithmetic, the locus of a circle, definition, examples, and more in this post on the locus.
Meaning of Locus
A locus is a collection of all points in a curve or surface that share an attribute. In mathematics, a locus is a collection of points that meet a set of certain rules, laws, or equations. We are all aware that the earth rotates in an elliptical orbit around the sun. This elliptical orbit is created by linking the earth’s positions at various times. The locus is the arc that connects all of the earth’s places in this example.
Every locus or curve is associated with an equation known as the locus equation. The supplied locus problem is used to create the curve and associated equation.
Locus
As stated previously, a locus is the location of all points that satisfy a condition. A circle, for example, is defined as the locus of points in the plane that are equally distant from a given point, and a sphere is defined as the same set of points in three-dimensional space that are equally distant from a given point.
The locus interprets any shape as an aggregation of points, such as a circle, parabola, ellipse, or hyperbola. The locus was the source of the word location.
Locus of Points
A locus of points is a group of points whose location is determined by a set of rules. A series of mountains in the northwest, for example, has been the site of several independence movements. The locus is the centre of any location in this case.
Only curved shapes are represented by the locus.
Regular or irregular shapes are possible. The locus is also displayed for patterns with a vertex or angle between them.
Theorems of Locus
In geometry, there are six basic locus theorems to consider. These theorems appear complicated at first glance, yet their concepts are straightforward. Let’s take a look at each one separately.
1st Locus Theorem
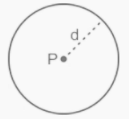
The locus at a given distance “d” from the point “p” is recognised as a circle, with “p” denoting the circle’s centre and “d” denoting the circle’s diameter.
The zone formed by all points that are at the same distance from a single point can be defined using this theorem.
2nd Locus Theorem
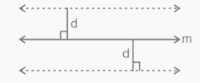
The locus is defined as a pair of parallel lines positioned on both sides of “m” at a distance “d” from the line “m” at a fixed length “d” from the line “m.” This theorem can be used to identify the region formed by all points that are at the same distance from a single line.
3rd Locus Theorem
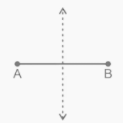
The loci that are equidistant from the two allocated points, “A” and “B,” are recognised as perpendicular bisectors of the line segment connecting the two places. The zone formed by all points that are at the same distance from points A and B is determined using this theorem. The perpendicular bisector of the line segment AB should be developed.
4th Locus Theorem
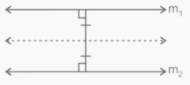
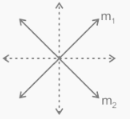
The locus that is equidistant from the two parallel lines, m1 and m2, is predicted to be a line parallel to both lines m1 and m2 and should be midway between them. This theorem can be used to determine the region formed by all points that are at the same distance from two parallel lines.
5th Locus theorem
The bisector of an angle is the locus that starts on the interior of the angle and is equidistant from the sides of the angle. This theorem is used to calculate the area formed by all points that are at the same distance from both sides of an angle. The angle bisector should be the area.
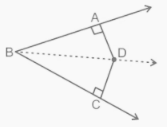
6th Locus Theorem
The locus that is equidistant from two intersecting lines; consider “m1” and “m2,” is identified as a pair of lines that bisects the angle formed by the two lines m1 and m2. This theorem is used to determine the region formed by all points that are the same distance apart from the two crossing lines. A pair of lines should be drawn that bisect the angle produced.
Conclusion
A locus is a collection of all points in a curve or surface that share an attribute. In mathematics, a locus is a collection of points that meet a set of certain rules, laws, or equations. The locus interprets any shape as an aggregation of points, such as a circle, parabola, ellipse, or hyperbola. The locus was the source of the word location. A locus of points is a group of points whose location is determined by a set of rules. Only curved shapes are represented by the locus. Regular or irregular shapes are possible. The locus is also displayed for patterns with a vertex or angle between them. In geometry, there are six basic locus theorems to consider. These theorems appear complicated at first glance, yet their concepts are straightforward.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






