A polygon is a two-dimensional geometry with at least three straight sides that intersect to form interior angles. They appear frequently in the world around us.
Because all simple polygons have as many sides as angles, the word “polygon” derives from the Greek meaning “many angles.” The triangle, the simplest polygon, has 3 inner angles. As a result, it has three sides.
Regular or irregular polygons are also possible. Regular polygons must be examined first in order to define an irregular polygon. A regular polygon is one that has the same length on all sides and the same number of interior angles. A three-sided regular polygon, for example, is a yield street sign.
What are regular and irregular polygons give one example for each
1. Regular polygons
The flat, closed, straight-sided object must also have another quality in order to be a regular polygon. In a regular polygon, every interior and exterior angle is equal to every other interior and exterior angle, and every side is the same length as every other side.
A regular polygon is a direct equiangular and equilateral polygon all sides have the same length Regular polygons contain convex or star-shaped polygons. If the perimeter or area is fixed, a sequence of regular polygons with an increasing number of sides approximates a circle in the limit or a regular apeirogon in the limit.
Regular polygon parts
There are three parts to a regular polygon:
Sides
Vertices
Angles: interior and exterior
Various types’ regular polygons
Regular polygons get their names from the number of sides they have.
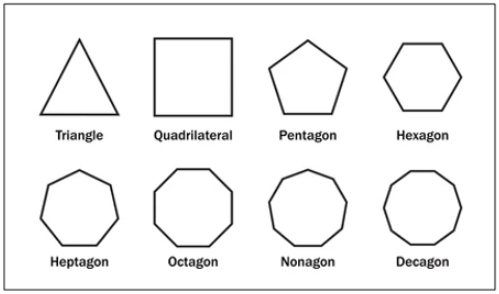
Figure 1: Examples of Regular polygons
Formula
The following formula can be used to compute each angle of a regular polygon
(n-2)×180°/n
where n is the number of sides in the regular polygon.
2. Irregular polygons
Irregular polygons have sides that are not equal in length and angles that are not equal in measure. As a result, they’re also known as non-regular polygons. In our daily lives, we see irregular polygons in the same way that we see regular polygons. An irregular polygon’s shape may not be as perfect as a regular polygon’s, but it is a closed figure with different side lengths. Scalene triangle, rectangle, kite, and other irregular polygons are examples. These two shapes are considered irregular polygons when the angles and sides of a pentagon and hexagon are not equal.
Some examples of irregular polygons are shown in the figure below.
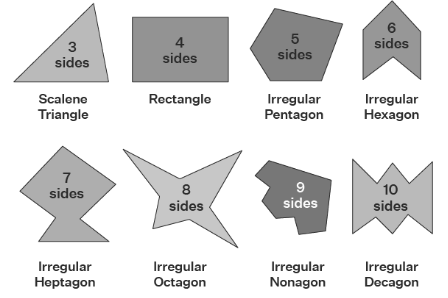
Figure 2: Examples of irregular
Formula
Simple formulas can be used to calculate the area and perimeter of irregular polygons.
Figure: 3
A flat closed shape with irregular sides and angles is known as an irregular polygon. In order to compute the area of irregular polygons, we first divide the irregular polygon into a collection of regular polygons whose area formulas are known. Consider the following scenario.
The ABCD polygon is a skewed polygon. As a result, the polygon ABCD can be divided into two triangles, ABC and ADC. The area of the triangle can be calculated as follows:
Area of polygon ABCD = Area of ∆ABC + Area of ∆ADC
Regular and irregular polygon and their properties
Regular Polygon Properties
A regular polygon’s sides and interior angles are all equal.
At the center of a regular polygon, the bisectors of the interior angles meet.
The lines connecting a regular polygon’s center to its vertices are all the same length.
The center of both the inscribed and circumscribed circles is the center of a regular polygon.
A regular polygon is divided into as many equal isosceles triangles as there are sides by straight lines drawn from the center to the vertices.
All perpendiculars drawn from a regular polygon’s center to its sides are equal.
Irregular Polygon Properties
Irregular polygons have a few unique characteristics that set them apart from other polygons. The properties are as follows:
An irregular polygon’s sides and angles are not equal, and irregular polygons might be convex or concave in nature.
Irregular polygons can be shaped in a number of different ways, both simple and complex.
Because their lengths are not equal, irregular polygons have infinitely large sides.
Irregular polygons, such as parallelograms, trapeziums, and quadrilaterals, are classed as such because their adjacent sides and angles are not equal.
Conclusion
We study that, Triangles (three sides), quadrilaterals (four sides), and pentagons (five sides) are the simplest polygons. All sides of a regular polygon are the same length, while not all sides of an irregular polygon are the same length. Polygon is a framework for creating block chain networks that are interconnected. It uses a revolutionary side chain solution to overcome some of the major shortcomings, such as low throughput, a poor user experience (slow transactions), and a lack of community governance. Polygons appear in practically every aspect of our lives, from fruits to honeycomb, from floor plans to rectangular or square-shaped structures. We use nut bolts with either a circular or hexagonal top.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






