In mathematics, a quotient is defined as the result of dividing an integer by any divisor. It refers to how many times the divisor appears in the dividend. As a result of dividing a number, we get a quotient. Division is a mathematical symbol ÷ that represents a way of evenly dividing things in groups. For example, there are 15 balls that must be evenly divided into three groups. As a result, when we split these balls into three equal groups, the division statement is 15 ÷ 3 = 5 the quotient in this case is 5. This means that each group will have five balls.
If division is the final step in evaluating an algebraic expression, it is called a quotient expression or an algebraic fraction. 5×2+5xx is a quotient expression, often known as an algebraic fraction.
Definition of a Quotient
A quotient is a quantity obtained by dividing two numbers in arithmetic. The quotient is a term that is widely used in mathematics to refer to the integer part of a division, a fraction, or a ratio (in the case of proper division).
The divisor is the number by which the dividend is divided. The quotient is the solution to the division issue.
How to Calculate a Number’s Quotient
- The first step in dividing correctly is to set up a division issue. Decide which number will be split first. That is the profit. Substitute it for the division bracket.
- The divisor, which goes to the left of the bracket, is the dividend divided by another number. Carry out the division. The quotient is your answer. Any leftovers are added to the right of the quotient.
- Finding the two specified components (dividend and divisor) in a word problem can be difficult, but these parts stand out in a numerical sentence. Consider the following sentence as an example. 35 ÷ 5 = ?
- In this situation, the complete number 7 would be our answer. As an example, the number 7 is a quotient.
Quotient derivative formula
In calculus, the quotient rule is a method for determining the derivative of any function given in the form of a quotient derived by dividing two differentiable functions. The quotient rule states that the derivative of a quotient is equal to the ratio of the result achieved by subtracting the numerator times the denominator’s derivative from the denominator times the numerator’s derivative to the square of the denominator’s derivative.
A formula for obtaining the derivative of a quotient of two functions is known as the quotient rule. It makes it a little easier to remember all of the terms. Let’s take a closer look at the formula.
If the numerator has the function f(x) and the denominator has the function g(x), the derivative is determined using the following formula:
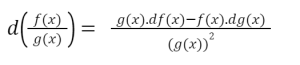
The d in this formula stands for derivative. As a result, df(x) and dg(x) denote the derivative of function f and function g, respectively. To obtain the derivative of f(x) divided by g(x), use the following formula:
Multiply g(x) by the derivative of f. (x).
Then subtract the product of f(x) times the derivative of g from that product (x).
After that, multiply those terms by g(x) squared
Quotient in algebraic expression
An algebraic expression is called a quotient expression or an algebraic fraction if division is the final step in evaluating it. A quotient expression, often known as an algebraic fraction, is 7×2+5xx.
A quotient algebra is the outcome of employing a congruence relation to partition the elements of an algebraic structure. Factor algebras are another name for quotient algebras.
A monomial that is equal to the quotient of two monomials’ numerical coefficients multiplied by the quotient of their literal coefficients is called a quotient of two monomials.
Quotient of two monomials = (quotient of their numerical coefficients) x (quotient of their variables)
Example:
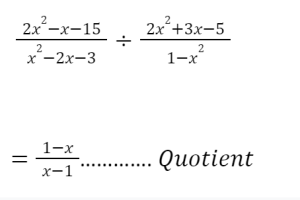
Conclusion
We study that, a quotient is a quantity that is obtained by dividing two numbers. The quotient is a term that is widely used in mathematics to refer to the integer component of a division, as well as a fraction or a ratio. The product rule is related to the Quotient rule. The ratio of the denominator quantity times the derivative of the numerator function minus the numerator times the derivative of the denominator function to the square of the denominator function is known as the Quotient Rule.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






