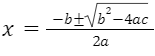The term quadratic is used in mathematics to refer to squares, the squaring operation, terms of the second degree, and equations or formulas that include such elements.
Quadratic equations have the form ax2+bx+c=0 and are 2nd -degree algebraic expressions. A quadratic equation is an “equation of degree two,” in other words. A quadratic equation is employed in a variety of situations.
Where the coefficients are a and b, the variable is x, and the constant term is c. The coefficient of x2 is a non-zero term a ≠0, which is the first criterion for an equation to be a quadratic equation. When writing a quadratic equation in standard form, the x2 term comes first, followed by the x term, and finally the constant term. The numeric values of a, b, and c are usually expressed as integral values rather than fractions or decimals.
Formula for a Quadratic Equation
The most established way for calculating the roots of a quadratic equation is to use the Quadratic Formula. Some quadratic equations are difficult to factor, and we can use this quadratic formula to acquire the roots as rapidly as possible in these circumstances. The roots of the quadratic equation can also be used to determine the sum of the roots and the product of the roots of the equation. The two roots of the quadratic formula are given as a single equation. Either the positive or negative sign can be used to get the equation’s two unique roots.
ax2+bx+c = 0
Quadratic equation’s roots
The two values of x obtained by solving the quadratic equation are the roots of a quadratic equation. The symbols alpha (α), and beta (β) are used to represent the roots of a quadratic equation. The 0 of the equation are also known as the roots of the quadratic equation.
Solving Quadratic Equations Methods
A quadratic equation can be solved to get two x values or the problem’s two roots. One of 4 methods can be used to get the roots of the quadratic equation. The following are the four ways for solving quadratic equations.
Factoring Quadratic Equations
Finding Roots Using Formulas
Completing Squares method
Finding Roots Using Graphing
Quadratics applications
Application of Quadratics given below:
Quadratic equations are used to solve many mathematical issues. The solution of the quadratic equation is particularly important in mathematics. If D < 0., a quadratic equation has no genuine solutions, as previously stated. This instance is crucial, as you will see in subsequent sessions. It contributes to the development of a different branch of mathematics known as Complex Analysis.
Quadratic formula are used in everyday life to compute areas, evaluate the profit of a product, and calculate the speed of an object. Furthermore, a quadratic equation is one that has at least one squared variable.
Quadratics multiple choice
Some Quadratics multiple choice examples given below
1. What are the roots of x2+2x-15
3,2
4,3
-5,3
-3,5
Answer: 3
Explanation – x2+2x-15
x2+5x-3x-15=0
x(x+5)-3(x+5)=0
(x-3)(x+5)=0
x=3, x=-5
2. If the roots of a quadratic equation are 20 and -7, calculate for the equation.
x2+13x-140=0
x2-13x-140=0
x2-13x+140=0
x2+13x+40=0
Answer: 2
3. The roots of the quadratic equation x2+20x+3=0 sum and product are?
-10,3
20,3
10,3
None of these are true.
Answer: 4
4. The quadratic equation x2 – 12x + a = 0 has three roots, one of which is thrice the other. Find out ithe value of a?
29
27
28
-7
Answer: 2
Conclusion
We study that, A quadratic equation is a second-degree equation, meaning it contains at least one squared element. ax2+ bx + c = 0 is the conventional form, with a, b, and c being numerical coefficients and x being an unknown variable. Quadratic formulas are used in everyday life to compute areas, determine a product’s profit, and determine an object’s speed. Furthermore, a quadratic equation is one that has at least one squared variable.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out