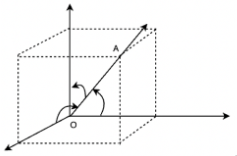
3D geometry is the study of shapes in three-dimensional space using three coordinates: x-coordinate, y-coordinate, and z-coordinate. To discover the exact location of a point in three dimensions, three criteria are necessary. A coordinate system is the technique of determining the position or location of a point on the coordinate plane in three dimensions.
Rectangular Coordinate System
Three parallel lines intersect at a common point. The origin is the common point, and the three lines are the axes. They are the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis. The observer’s position in relation to any other point is measured by O. The position or coordinates of any point in three-dimensional space are determined by how far he has traveled along the x, y, and z-axes.
Point, Line and Plane
There is no attempt to define points, lines, or planes because they are fundamental notions. They do, however, have qualities that may be precisely articulated. Two distinct points determine one line. That line is the shortest route between the two points. One and only one plane is determined by three non-collinear points.
Distance of a Point From Origin
Using the Pythagorean theorem The distance between P (x,y,z) and the origin O (0,0,0) is
d = √(x2+y2+z2)
Distance Between 2 Points in Space
Using the Pythagorean theorem The distance between P (x1,y1,z1) and the Q (x2,y2,z2) is
d = √((x2-x1)2+(y2-y1)2+(z2-z1)2)
Point Dividing Line Segment Joining Two Points
Let R be a point which divides the line segment PQ between two points P (x1,y1,z1) and the Q (x2,y2,z2) internally with ratio m:n then the coordinates of R are:
((mx2+nx1)/(m+n), (my2+ny1)/(m+n), (mz2+nz1)/(m+n))
A Line Segment Projected in Three Dimensions
Assume that AB is a line segment. Then its projection on line PQ is ABCosθ
Note: The line can extend in both directions, and it can produce two different angles with the coordinate axes. The line makes α, β, and γ and their supplements π-α, π-β, and π-γ with the coordinate axes. The directional cosines’ indications will now be flipped. We chose to make it a directed line in order to have unique directional cosines.
Let’s say the lines’ directional cosines are l, m, and n.
Ratios of Direction
Direction ratios of the line are numbers that are proportional to the line’s direction cosines. The directional cosines of the lines are assumed to be l, m, and n. Let’s say the line’s directional ratios are a, b, and c. Then,
l = k × a, m = k × b and n = k × c
Where k is any constant.
Cauchy Schwarz Inequality
One of the most important and extensively used inequalities in mathematics is the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality (also known as the Cauchy–Bunyakovsky–Schwarz inequality). Augustin-Louis Cauchy published the inequality for sums (1821). Viktor Bunyakovsky (1859) and Hermann Schwarz (1859) published the analogous inequality for integrals (1888). The integral version was modernized by Schwarz.
According to the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality, for any vectors u and v in an inner product space,
{ u, v } 2 ≤ { u, u} + { v, v}
Conclusion
Three-dimensional space is a geometric setting in which the position of an element is determined by three values. This is how the term dimension is commonly used. A tuple of n numbers can be thought of as the Cartesian coordinates of a point in n-dimensional Euclidean space in mathematics.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out