A line segment is a piece, or part, of a line. The line segment is represented by endpoints on each end of the line segment. A line in geometry is represented by a line with arrows at each end which goes on forever. A line segment and a line are different because a line goes on forever while a line segment has a distinct beginning and end and it is measurable. In other words, A line segment is a track between two points that can be measured. Since line segments have a defined length, they can form sides of any polygon.
LINE SEGMENT-
A line segment is represented by a bar on top of the edge name which is the line segment symbol. It is written as ¯¯¯A ¯¯B¯¯
HOW TO MEASURE LINE SEGMENTS?
Line segments can be measured with the help of a scale or ruler. Let us see how to measure a given line segment PQ.
- Step 1: Place the tip of the ruler/scale carefully so that zero is placed at the starting point P of the line segment.
- Step 2: Now, start reading the values in the ruler on the ruler and spot the number which comes on the other endpoint of the line Q.
- Step 3: Thus, the length of the line segment PQ is 4 inches, which can be written as ¯¯¯¯P¯¯Q¯¯¯ = 4 inches.
LINE SEGMENT FORMULA-
In the above example, we measured the length of line segment PQ which was 4 inches. Now, let us see how to find the length of a line segment when the coordinates of the two endpoints are given from a graph. In this case, we will use the distance formula, that is, D = √[(x2−x1)2 + (y2−y1)2] . Here, (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of the given points.
For example, let us consider the line segment has the following coordinates: (-2, 1) and (4, –3). Now Let us apply the distance formula to find the length of the line segment formed by those points. Here, x1 = -2; x2 = 4; y1 = 1; y2 = -3 After substituting the values in the distance formula we get: D =√[(4-(-2))2 + (-3-1)2) = √((4+2)22 + (-3-1)2] = √(62 + (-4)2) = √(36 + 16) = √52 = 7.21 units. Thus, using the distance formula, we found that the length of the line segment with the given coordinates (-2, 1) and (4, –3) is 7.21 units.
Difference Between Line, Line Segment, and Ray
In order to understand the difference between a line, a line segment, and a ray, below is the description of the line, line segment, and ray.
LINE–
- Line is defined as the set of points that can be extended in two opposite directions.
- It is represented with arrows at both ends to tell us that it can be extended indefinitely.
LINE SEGMENT-
- A line segment is a part of a line that has a beginning as well as an endpoint.
- It is represented with two endpoints and has a definite length.
RAY–
- A ray is a part of a line. Ray has a starting point but no endpoint.
- It can be denoted by one start point and on the other end an arrow which means that it goes on forever through one direction.
FEW FACTS ABOUT THE LINE SEGMENT-
- A line has no ends and cannot be measured.
- A line segment has a start point and an endpoint, therefore, it can be measured.
- Line segments have a defined length, thus, they can form the sides of any polygon.
- A ray has just one start point but no endpoint, therefore, it cannot be measured.
- The concept of rays can be understood with the example of the rays of the sun, which have a beginning point but no endpoint.
CONCLUSION-
A line segment is a piece, or part, of a line. The line segment is represented by endpoints on each end of the line segment. A line in geometry is represented by a line with arrows at each end which goes on forever. A line segment and a line are different because a line goes on forever while a line segment has a distinct beginning and end and it is measurable. In other words, A line segment is a track between two points that can be measured. Since line segments have a defined length, they can form sides of any polygon.
- A line has no ends and cannot be measured.
- A line segment has a start point and an endpoint, therefore, it can be measured.
- Line segments have a defined length, thus, they can form the sides of any polygon.
- A ray has just one start point but no endpoint, therefore, it cannot be measured.
- The concept of rays can be understood with the example of the rays of the sun, which have a beginning point but no endpoint.

- If the lengths of the conjugate and transverse axes are similar, then a hyperbola is equilateral or rectangular.
- Asymptotes of the hyperbola are where two lines intersect at the centre of a hyperbola.
- The line perpendicular to the transverse axis and passing through any of the foci, which are parallel to the conjugate axis, is the latus rectum of the hyperbola.
Types of Hyperbola
There are two types of hyperbola: Horizontal Hyperbola and Vertical Hyperbola.
- Horizontal Hyperbola: In this type of hyperbola, the conjugate’s axis is the x-axis, and the standard formula with the centre (0, 0) is:

Where,
- the coordinates of the vertices = (a, 0)
- the coordinates of the co-vertices = (0, b)
- the coordinates of the foci = (c, 0)
- the length of the transverse axis = 2a
- the length of the conjugate axis = 2b
- the distance between the foci = 2c, where, c2= a2 + b2
- the equations of the asymptotes = y = bax
2. Vertical Hyperbola: In this type of hyperbola, the conjugate’s axis is the y-axis, and the standard formula with the centre (0, 0) is:

Where,
- the coordinates of the vertices = (0, a)
- the coordinates of the co-vertices = (b, 0)
- the coordinates of the foci = (0, c)
- the length of the transverse axis = 2a
- the length of the conjugate axis = 2b

Problems on Hyperbola
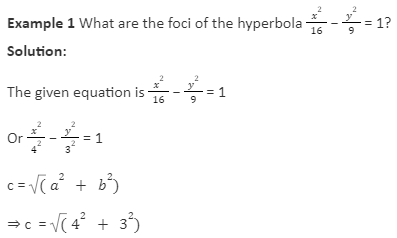
c= ( 16 + 9)
=25
= 5
The foci of hyperbola (± c , 0)
(± 5 , 0)
Example 2: For the given equation below, find the coordinates of the vertices, the foci, the eccentricity, and the length of the latus rectum of the hyperbolas:

Example 3: Find the equation of the hyperbola with foci (0, ± 5) and vertices (0, ± 3 ).

1
Since vertices are (0, ± 3 ), a = 3
Also, since foci are (0, ± 5); c = 5
c = ( a2 + b2)
5 = ( 32 + b2)
Squaring both sides
52 = 32 + b2
25 = 9 + b2
b2 = 25 – 9
b2 = 16
b = 16
b = 4

Conclusion
In the above article, we have defined the basics of Hyperbola along with its properties, types and so on. Hyperbola is an open curve formed by the intersection of a circular cone with a plane at a smaller angle in a symmetrical manner. It has two axes of symmetry. Besides, there are two types of Hyperbola – Horizontal Hyperbola and Vertical Hyperbola.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






