An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length and a third of varying length. In mathematics, the isosceles triangle theorem says that the angles opposite the equal sides of an isosceles triangle are also equal in measurement. This article will cover the isosceles triangle theorem and its converse.
Isosceles Triangle Theorems
According to the isosceles triangle theorem, if two sides of a triangle are congruent, then their opposing angles are likewise congruent.
Properties, Characteristics, and Applications of the Isosceles Triangle
Numerous triangles found in the real world, like a part of a slice of pizza, can be called isosceles. Frequently, complex or sophisticated forms are deconstructed into simpler ones, such as triangles.
The two parallel sides are referred to as the legs, while the third side is referred to as the foundation. Frequently, a problem will employ this phrase in order to convey facts.
Knowing that an isosceles triangle has two equal sides brings us to the first isosceles triangle theorem. Now, let’s learn how to locate and compute the missing sides of an isosceles triangle.
The following are some fundamentals of the isosceles triangle:
- The triangle has two equal sides and a third uneven side, which is the base.
- The angles on the opposite sides of two equal sides will always be same.
- When the third angle of an isosceles triangle is 90 degrees, it is referred to as a right isosceles triangle.
Facts for Isosceles Triangle
- The term ‘isosceles’ comes from the Latin word isosceles’ and the ancient Greek word ‘o (isosceles),’ which means ‘equal-legged.’
- Babylonian and Egyptian mathematics were well acquainted with the concept of ‘area’ long before Greek mathematicians investigated the isosceles triangle.
- Isosceles-shaped buildings are not only gorgeous, but also earthquake resistant.
- Due to their exceptional strength, the forms of this triangle are frequently used in construction.
- Always keep in mind that the total of the isosceles triangle’s three angles is always 180 degrees. Thus, if the values of two angles are known, determining the value of the third angle is straightforward.
Isosceles Triangle
Here we have on display the majestic isosceles triangle, △DUK. You can draw one yourself, using △DUK as a model.
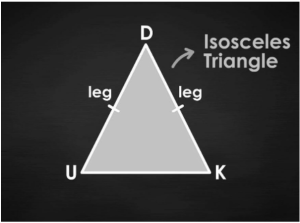
Hash marks show sides ∠DU ≅ ∠DK∠DU ≅ ∠DK, which is your tip-off that you have an isosceles triangle. This is an isosceles triangle if the two sides, called legs, are equal.
Properties of an Isosceles Triangle
Let’s utilise △DUK to explore the components:
- △DUK , like every triangle, has three internal angles: ∠D, ∠U, and ∠K.
- Each of the three internal angles is acute.
- △DUK , like every other triangle, has three sides: DU, UK, and DK.
- ∠DU ≅ ∠DK, so we refer to those twins as legs
- The third side is referred to as the base (even when the triangle is not sitting on that side)
- The two angles created by the base and legs, ∠DUK and ∠DKU, or simply ∠D and ∠K, are referred to as base angles.
Isosceles Triangle Theorem
Having identified the triangle’s constituents, here is the problem: how can we demonstrate that the base angles are congruent? That is the essence of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem, which is constructed as an if-then statement:
To demonstrate this mathematically, we need to add a median line, which is a line drawn from an inner angle to the opposing side’s midway. On base UK, we locate Point C and create the line segment DC:
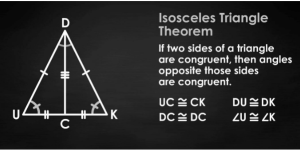
There! That is simply DUCKy! Consider the two triangles that the median creates. We are given the following:
- UC ≅ CK (median)
- DC ≅ DC (reflexive property)
- DU ≅ DK (given)
We have just demonstrated that the three sides of △DUC are congruent with △DCK, implying the existence of the Side Side Side Postulate, which establishes congruence. Therefore, if two triangles are congruent, their corresponding portions are also congruent (CPCT), which indicates:
- ∠U ≅ ∠K
The Isosceles Triangle Theorem’s inverse
The reverse of the isosceles triangle theorem argues that if two triangle angles are congruent, then their opposing sides are equal. This is precisely the converse of the theorem mentioned above. As explained below, we shall use the isosceles triangle’s characteristics to demonstrate the converse.
Conclusion
As previously stated, an isosceles triangle is defined as one with two congruent sides. Additionally, it features two congruent angles. The isosceles triangle theorem’s converse states that a triangle with two equal angles will have two equal sides.
As a result, we may identify an isosceles triangle in two ways: whether it has two congruent sides or if it has two congruent angles. Knowing one of these qualities establishes the triangle’s isosceles nature.
In the final example, we will establish the isosceles nature of a given triangle.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






