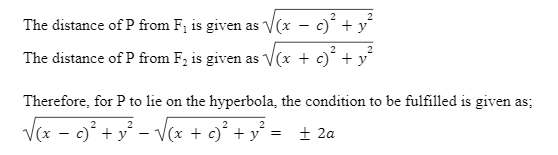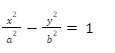A hyperbola is a special shape that is part of the three shapes that can be formed when a cone in a three-dimensional field is intersected by a plane. The other two shapes formed when a plane intersects the cone are the ellipse and the parabola.
The parabola and the ellipse are single curves, but the hyperbola is a shape made up of two curves. These two curves are symmetric and are similar to the shape of an infinite bow. A hyperbola is created at the intersection of a double cone by a plane, but at an angle such that the cone’s apex does not lie on the plane.
A hyperbola is also called a locus of points geometrically. The locus of points is created such that any point that belongs in the set of all the points present on the hyperbola will fulfill a particular property. The property is that the absolute difference of the point from two certain points that form the hyperbola’s pair of foci is a constant. For example, if F1 and F2 are the two foci of the hyperbola and PF1 and PF2 are the distances from P to F1 and F2, respectively, then |PF1–PF2| is a constant for any point P.
Each bow in the hyperbola is called a branch, and each branch has a focus and a vertex. Let us now have a look at the equation of a hyperbola.
The equation of a Hyperbola
Let us consider a hyperbola with two vertices on the x-axis, V1 and V2, the coordinates of which are (a,0) and (-a,0). The hyperbola will also have two foci that lie on the x-axis, F1 and F2, and those coordinates are (c,0) and (-c,0). Let us assume any point P at coordinates (x,y). For this point P to be on the hyperbola, the absolute difference of the distances of point P from F1 and F2 should be a constant equal to 2a.
Properties of a Hyperbola
A hyperbola is drawn on a cartesian plane concerning specific points that play a special role in defining the shape and structure of the hyperbola.
Vertex
The vertex is defined as the point where the two branches of the hyperbola intersect the major axis of the hyperbola. Each branch is a mirror image of each other. Therefore, both the vertices are at an equal distance from the plane’s origin. The constant equal used to find a point on the hyperbola from the foci is equal to the distance from one vertex of the hyperbola to the other.
Focus
Each branch that forms a part of the hyperbola is drawn concerning a focus. Every hyperbola has a pair of foci that are at an equal distance from the plane’s origin. If there are two foci, F and G, of a hyperbola, then the distance of a point P, which is on the branch whose focus is F, from the focus F will always be less than the distance from the focus G and vice versa.
Asymptotes
As we move away from the vertex of a branch in a hyperbola, the line keeps getting straighter and straighter. The limits of the diagonally opposite ends of the two branches tend to a common line. This line is called the asymptote of the hyperbola. There are two asymptotes to any hyperbola. These asymptotes intersect each other at the point which is the center of symmetry for the two branches of the hyperbola.
Example of Hyperbola
A spacecraft is zooming through black, empty space, just a speck in the sea of stars surrounding it, traveling towards its landing planet, Planet H. When suddenly the captain of the ship realizes they need to make a U-turn, because they missed planet H and traveled a bit forward. There is a planet G in front of them, and the captain decides she is going to slingshot the spaceship around planet G.
As they approach the planet G, the spacecraft uses the gravity of the planet G to get into orbit, make a U-turn and then launch themselves out of the orbit towards planet H. If you trace the path of the spacecraft around the planet G, you will end up with a special shape or a conic section, called the Hyperbola.
Conclusion
A hyperbola is a special shape that is part of the three shapes that can be formed when a cone in a three-dimensional field is intersected by a plane. The hyperbola is a shape made up of two curves. These two curves are symmetric and are similar to the shape of an infinite bow. A hyperbola is created at the intersection of a double cone by a plane, but at an angle such that the apex of the cone does not lie on the plane.
Each bow in the hyperbola is called a branch, and each branch has a focus and a vertex. Let us assume any point P. For this point P to be on the hyperbola the absolute difference of the distances of point P from F1 and F2 should be a constant equal to 2a.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out