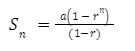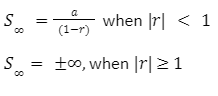A geometric sequence is one in which each subsequent element is derived by multiplying the preceding element by a constant known as the common ratio, indicated by r. The formula x sub n equals a times r to the n – 1 power, where a n the first term in the sequence and r is the common ratio, yields the general term, or nth term, of any geometric sequence. We utilize this formula because writing out the sequence until we reach the required number is not always possible. Divide any term by the preceding term to get the common ratio (r). An arithmetic sequence’s general term can be represented as a n =a1+(n-1)d in terms of its initial term a1, common difference d, and index n.
General Term
We can use a formula to find the general term, or nth term, of any geometric series. x sub n = a times r to the n – 1 power is the formula.
x n = ar n-1
The number in that series is represented by x sub n in this formula. The fourth term in our sequence is denoted by x sub 4. The letter n stands for the term in question. We are seeking for the tenth term in our sequence if n is 10. The r stands for the common ratio, which is the multiplication constant used to calculate each consecutive integer or term in the geometric sequence. When we want to utilize this formula, we enter our a and r for our geometric sequence.
nth term of a geometric progression
Proof: If each term in the geometric series, such as a1, a2, a3, a4,….am,….an, is represented by the first term a1, the terms in the geometric series will be as follows:
a1 = a1
a2 = a1r
a3 = a2r = (a1r) r = a1r²
a4 = a3r =( a2r²) = r = a1r³
an = a1rn-1
Geometric Progression formula sum to infinity
A geometric progression’s sum of infinite GP is the sum of an infinite number of terms (GP). We may believe that the sum of an infinite number of terms will always be infinite. In the case of an infinite GP, however, this is not the case. When the absolute value of the common ratio is less than 1. The sum of infinite GP is a finite number.
The sum of infinite GP is just the sum of infinite Geometric Progression. A limited infinite GP can exist.
The formula for calculating the sum of an infinite GP’s first ‘n’ terms is:
where ‘a’ stands for the first term and ‘r’ stands for the GP’s common ratio.
When |r| < 1 the sum of infinite GP
Consider a general professional whose first term is ‘a’ and whose common ratio is ‘r,’ with |r| < 1. . Then its infinite terms add up to:
S = a + ar + ar² + ar³+ …___ (1)
‘r’ multiply both sides:
rS = ar + ar² + ar³ + …___ (2)
(2) is subtracted from (1):
S – rS = a
S (1 – r) = a
Both sides are divided by (1 – r),
S = a / (1 – r)
This is the formula for infinity GP when r is less than 1.
When |r| ≥ 1 the sum of infinite GP
When |r| ≥ 1,1, the GP is 2, 4, 6, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, and so on, where the numbers keep increasing and eventually become very huge numbers. As a result, the total of a GP where |r| is bigger than 1 cannot be calculated, and the series diverges in this instance.
The sum of GP formulae can be summarized as follows:
The first term is ‘a,’ while the common ratio is ‘r.’
Conclusion
Geometric progression, also known as a geometric sequence, is a sequence of non-zero numbers. Each term following the first is found by multiplying the previous one by the common ratio, which is a fixed, non-zero value. A geometric sequence is a set of integers in which each number is obtained by multiplying the preceding number by a constant. We divide each number by the previous number to see if it’s a geometric sequence.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out