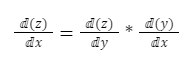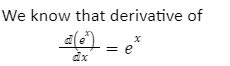In mathematics, Differentiation is the part of differential calculus in which we study the rate of change of the function.
Definition
Differentiation can be defined as the process of determining a derivative of the given function which further means the rate of change of that function.
Differentiation is a technique for determining a function’s derivative. Differentiation is a mathematical procedure that determines the instantaneous rate of change of a function based on one of its variables. The most common example is velocity, which is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time.
In Geometry, the slope of the tangent line at some point of the curve is the derivative of that curve at that point, provided the derivative exists at that point.
The use of Differentiation is not limited to mathematics only, it is widely used in physics as well as in chemistry. For example, In physics, we know that acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time, which means that If we need to calculate the acceleration, we have to differentiate the velocity with respect to time.
Differentiation can also be defined as the ratio of a slight change in one variable to a tiny change in another that is dependent on the first quantity. One of the most essential ideas in calculus is the differentiation of a function.
Symbol, Formula and Rule
Let’s say, we have a function f(x) and we need to find the rate change of f(x) with respect to time “t”,
![]()
In Differentiation, there are many numbers of formulae we use, majorly are of three types i.e.

- Exponential Function: dfx/dt, where fx is the Exponential Function
d(ex)/dx=ex
There are some rules which help us to solve differential problems
- Power Rule: If f(x) = xn then, dfx/dt = nxn-1.
- Sum Rule: (d/dx) (f ± g) = (f’ ± g’).
- Product Rule: (d/dx) (fg)= (fg’ + gf’).
In calculus, the product rule is a method for determining the derivative of any function given in the form of a product produced by multiplying any two differentiable functions.
- Quotient Rule: (d/dx) (f/g) = [(gf’ – fg’)/g^2]
According to the Quotient Rule, the derivative of a quotient equals the denominator times the numerator’s derivative minus the numerator times the denominator’s derivative, all divided by the denominator’s square.
Chain Rule: It is used to compute the derivative of the composition of two or more functions.
Conclusion
Differentiation is the process of finding the derivative of the given function, it can be used in various fields and majorly used to find the slope of any curve and rate change of any function.
Derivative of a constant function is zero(0)
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out