Continuity and differentiability are important topics that students should know. To understand these topics in a better way, we will first see the definition of both Continuity and Differentiability.
In mathematics, Continuity is the conceptual model of the intuitive idea of a curve that develops without unexpected breaks or leaps. In calculus, differentiability is a one-variable function whose derivative exists at every point in its area.
Let us learn more about Continuity and Differentiability in detail by learning them separately.
Continuity
In mathematics, a continuous function is one in which a continuous variation in the argument, such as no gap or leap, causes a continuous variation in the function’s value. This signifies that there are no discontinuities or abrupt changes in value. A function is continuous if it can guarantee indefinitely minor changes in its value by restricting its argument to sufficiently small changes.
Continuity is a fundamental idea in calculus and mathematics, where real and complex numbers are used as inputs and values of functions. The concept has been extended to include functions between metric and topological spaces. The latter is the most basic continuous function, and topology is founded on their formulation.
Three conditions must be fulfilled for a function f(x) to be called continuous. They are as follows:
- The value of f(a) should be limited. At this point, the function should have a defined value. We would claim that f(x) exists in mathematical terms.
- The right-hand limit should equal the left-hand limit, and both should not be infinite.

Finally, at this stage, the limit must equal f(x).
What is a function’s limit?
A function’s limit is the y-value that a function approaches as a graph approaches an x-value. There are limits to Continuity:

We say the limit of the function as x approaches an occurs and is equivalent to the one-sided limits if the left and right limits exist (are not infinite) and are equal. Then this is how we write it.
Discontinuity
If the conditions are not met, then there will be discontinuity. A discontinuous function is a graph function that is not connected to other graph functions. There are three types of discontinuities:
- Removable Discontinuity- A removable discontinuity is a graph point that is undefined or does not connect with the rest of the graph. When you look at the graph, there is a break at that point. A removable discontinuity on a graph is marked by an open circle at the spot where the graph is indeterminate or has a different value.
- Jump Discontinuity- Jump Discontinuity is a category of discontinuities in which a function skips, or jumps, from one spot to another along its curve, typically breaking the curve into two parts. Although continuous functions are frequently employed in mathematics, they are not all continuous. The discontinuity is a point on a function’s domain that is discontinuous.
- Infinite Discontinuity-An infinite discontinuity has one or even more infinite limits, which are numbers that increase in size as you get closer to the function’s gap. An infinite discontinuity is a type of essential discontinuities that are a large group of misbehaving discontinuities that can’t be removed.
Differentiability
In calculus, a differentiable function is a one-variable function whose derivative exists at every point in its domain. At each interior point in a differentiable function’s domain, the tangent line to the graph is always non-vertical. There is no break, crest, or angle in a differentiable function. A differentiable function is always continuous; however, not every continuous function is differentiable.
Differentiation is essential, and being able to assess whether or not a function is differentiable is a crucial skill. The derivative of a function is sometimes referred to as the “instantaneous rate of change” since it measures the rate of change of the function value concerning its input.
Rules for differentiating functions:
If f and g are differentiable functions, we may compute the derivatives of their sum, difference, product, and quotient using some rules. Here are various differentiability formulas for finding a differentiable function’s derivatives:
- (f + g)’ = f’ + g’
- (f – g)’ = f’ – g’
- (fg)’ = f’g + fg’
- (f/g)’ = (f’g – fg’)/f²
Conclusion
The condition of differentiability is more powerful than the criterion of Continuity. If f can be differentiated at x=a, it can also be continuous at x=a. The opposite, on the other hand, does not have to be true.
The only requirement for f’s continuity at x=a is that f(x)-f(a) converges to zero as x→ a.
That difference must converge even after being divided by x-a to be differentiable. To put it
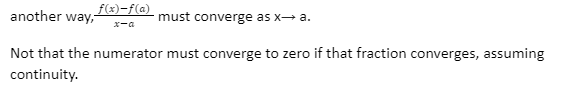
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






