As we all know, integration is the process of computing the area of a region by dividing it into several primary strips and then adding the total areas of these elementary strips. At this point, we can calculate the area enclosed by a curve and a line connecting a given set of points. You will learn how to find the enclosed area between two curves in calculus in the following discussion, which will include two situations and several examples.
Area Between Two Curves
We already know that the area of a planar lamina is the amount that is used to express the region inhabited by the two-dimensional structures in the plane. It is important to determine the difference of definite integrals of a function in calculus in order to evaluate the area between two curves. For two curves or functions to be connected, the area between them is defined as the definite integral of one function, such as f(x), less the definite integral of another function, such as g(x), with the lower and higher bounds denoted by a and b, respectively. As a result, the following can be used to represent it:
Area between two curves = b∫a [f(x) – g(x)] dx
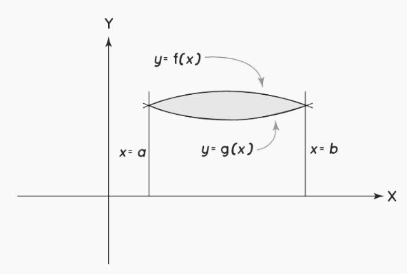
Area Between Two Curves Formula
For example, if we want to find the approximate area between two curves, we must divide the area into many small rectangular strips parallel to the y-axis, starting from x = a and progressing to x = b. Then, using integration, we can add the areas of these small rectangular strips to obtain the approximate area between the two curves. Dx and f(x) – g(x) are the width and height of these rectangular strips, respectively (x). The area of the small rectangular strip is given by dx(f(x) – g(x)), and we can now compute the area between these two curves by integrating within the bounds of x = a and x = b using the integration formula. If f(x) and g(x) are continuous on [a, b] and g(x) < f(x) for every x in [a, b], then the following formula can be used to find f(x) and g(x).
Area = b∫a [f(x) – g(x)] dx
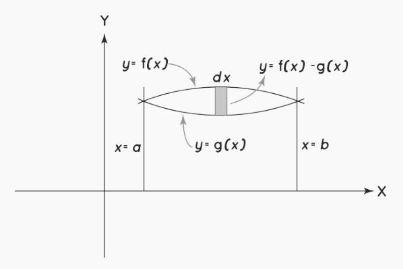
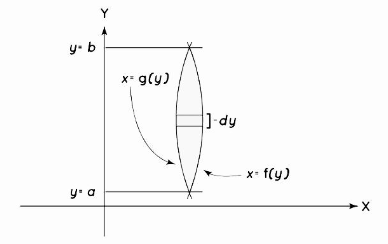
Area Between Two Curves with Respect to Y
The method of computing the areas of the curves whose equations are given in terms of y is the area between two curves with regard to the y-axis, which is also known as the area between two curves with respect to the y-axis. When compared to calculating the area along the x-axis, calculating the area along the y-axis is less difficult to do. We divide the given region into horizontal strips between the specified limitations, and we use integration to add the areas of the horizontal strips in order to obtain the area of a section between two curves that lies within the given limits. It follows that if f(y) and g(y) are both continuous on [c, d] and that g(y) < f(y) for all the variables in [c, d], then
Area = b∫a [f(y) – g(y)] dy
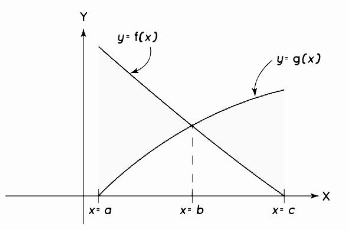
Area Between Two Compound Curves
Calculating the area between two compound curves that meet with each other using the above-mentioned formulas will result in an inaccurate result, and the curves will be shifted after the intersection occurs. We separated the intervals between the curves in the image into different sections and then calculated the individual areas between the curves in each part for the curves seen in the image. If f(x) and g(x) are both continuous in the [a,b] interval, then the area between the curves will be as follows: [a,b]
Area = c∫a |f(x) – g(x)| dx
As we see in the region [a, b], f(x) ≥ g(x) and in the region [c, d] g(x) ≥ f(x), so we break the limits into two parts as:
Area = b∫a [f(x) – g(x)] dx + c∫a [g(x) – f(x)] dx
Area Between Two Polar Curves
With the use of integral calculus, we can also find out how much space is between two polar curves. In this method, we have two curves whose coordinates are not given in rectangular coordinates but rather in polar coordinates, and their coordinates are given in rectangular coordinates. To tackle this problem, we can always convert the polar coordinates to rectangle coordinates, but we can utilise this method to lessen the complexity of the problem. Imagine that we have two polar curves, represented by the lines in the image, and that we wish to discover the area enclosed between these two curves such that ro = f(θ) and ri = g(θ) and where [α, β] is the bounding region of the bounded region. The area between the curves will therefore be as follows:
A = 1/2 β∫α (2ro–2ri)dθ
Examples of Area Between Two Curves
Example 1: Find the area between two curves f(x) = x² and g(x) = x³ within the interval [0,1] where f(x) ≥ g(x) in the given region.
Solution: Given: f(x) = x² and g(x) = x³
Using the formula for the area between two curves:
Area = b∫a [f(x) – g(x)] dx
Area = 1∫0 [x²-x³]dx
= 1[⅓x³ – ¼x⁴]0
= ⅓ – ¼
= 1/12
Conclusion
An important application of integration is the determination of the area between two curves. We have learned to determine the area under a curve by using integration; in the same way, we have learned to calculate the area between two intersecting curves by using integration. It is the area of space that lies between two linear or non-linear curves within the specified limitations of their distance from each other. The area between two curves can also be composite, but we can easily obtain that by integrating the two curves together and using simple adjustments to the well-known methods for calculating the area under two curves.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






