Introduction:
When two lines intersect at any point, an angle is firmed. The ‘angle’ can be defined as the measurement of the ‘opening’ between these two rays. It is symbolised by the sign. The Angles are commonly measured in degrees and radians, which are measures of circularity and rotation. Angles are a common occurrence in our day to day life. Angles are used by engineers and architects to create roads, buildings, and sporting facilities.
Angle is derived from the Latin term angulus, which means “corner,” and is related to the Greek o (ankylos), which means “crooked, bent,” and the English word “ankle.” Both have the Proto-Indo-European root *ank-, which means “to bend” or “bow.” A plane angle is defined by Euclid as the inclination in a plane of two lines that intersect and do not lay straight with respect to each other. An angle must be either a quality or a number, or a connection, according to Proclus. Eudemus uses the first notion, viewing the angle as a departure from the straight line; Carpus of Antioch used the second concept, viewing an angle as the interval or space between intersecting lines; and Euclid used the third model. [3], and do not lie in a straight line with each other
Let’s have a look at the various components of an angle.
Angle Components
The two main components of an angle are Arms and Vertex.
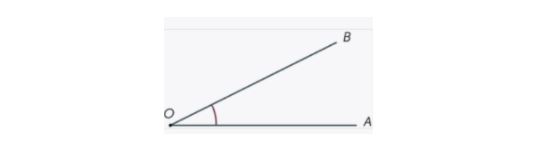
- The Angle’s Arms: The arms of the angle are the two rays that meet at the same point to produce the angle. Look at the diagram below, which illustrates that the angles OA and OB are the arms of the angle AOB.
- The Angle’s Vertex: The two rays have a common terminal point that can be called the vertex. Look at the figure, where the vertex O is designated as the location where the two arms intersect.
Angle measurement
A degree is a unit of measurement for an angle. A complete 360° angle is formed by one full rotation around a point.
A protractor is the greatest tool for measuring angles. A protractor is a measuring tool that is shaped like a semi-circle. It’s a transparent tool for measuring angles in degrees.
Angle Types and Their Properties
An angle is formed when two rays or lines meet at a similar point, and each angle has a different measure. Acute angle, right angle, obtuse angle, reflex angle, and straight angle are all examples of angles in geometry. An acute angle is one that is less than ninety degrees, while an obtuse angle is one that is higher than 90 degrees. Angle pairs come in a variety of shapes and sizes. There are six different kinds of angles. On the basis of angle measurement, each sort of angle has its own unique identifier. Let’s take a look at each sort of angle and its characteristics one by one.
- Acute Angle
An acute angle is one that is larger than 0° but less than 90° in length.
- The Right Angle
A right angle is defined as one that measures 90 degrees. A right angle is immediately identifiable because it takes the shape of the letter L.
- Obtuse Angle
An obtuse angle can be defined as an angle that is less than 180 degrees but higher than 90 degrees.
- A Straight Angle
A straight angle can be defined as the angle formed by a straight line. To put it another way, a straight angle is a straight line, and the angle generated by two rays is 180°. The two rays are opposite each other at a straight angle. Two right angles make one straight angle. A straight angle is one-half of a circle’s turn because its measurement is 180°.
- Reflex Angle
A reflex angle can be defined as the angle that is larger than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.
- Complete Angle
It is a complete angle that can be defined as the angle equals 360°.
Angle Determined by Rotation
Angles can be divided into two sorts based on the direction of measurement or rotation:
- Positive Perspectives
- Negative Perspectives
- Positive Perspectives
A positive angle is one that is measured in the counterclockwise (anti-clockwise) direction. Positive angles, in other words, are those that are rotated in an anti-clockwise manner from the base.
2.Negative Perspectives
The Negative angles are those that are measured from a base in a clockwise manner. Also, it can be understood that negative angles are angles that are rotated in the clockwise direction from the base.
Points To Remember-
- Complementary angles: Two given Angles whose sum is 90.
- Supplementary angles: Two given Angles whose sum is 180.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






