The inorganic compound BF3 stands for boron trifluoride. It’s a very poisonous, colorless, non-flammable gas with a distinct, penetrating odor. It readily dissolves in water and other organic substances that include nitrogen or oxygen.
It may be slowly hydrolyzed by cold water to produce hydrofluoric acid, and it can also be hydrolyzed in moist air to produce white thick vapors. Its vapors have a higher density than air. Inhaling the gas irritates the respiratory system, and if the gas comes into contact with the skin in high amounts, it can cause burns.
What is the Hybridization of Boron Trifluoride?
In its ground state, BF3 includes a boron atom with three outer-shell electrons and three fluorine atoms with seven outer electrons. In addition, one boron electron is unpaired in the ground state.
The 2s orbital and two 2p orbitals hybridize during the synthesis of this molecule. As the lone pair, just one of the vacant p-orbitals remains. Boron requires three hybridized orbitals to create bonds with three atoms of F, where the 2pz orbitals overlap with the hybridized sp2 orbitals, resulting in bonds.
BF3 Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles
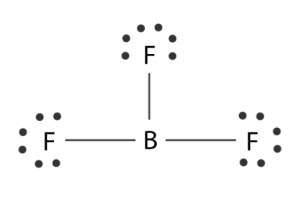
Boron creates monomeric covalent halides with a planar triangular shape in its natural state. The overlap of the orbitals between the two molecules is primarily responsible for this shape. The molecular geometry of BF3 is trigonal planar, to be precise. It is also nonpolar and has symmetric charge distribution on the central atom.
When all of the atoms are in one place, the bond angle is 1200. They all form an equilateral triangle as well.
Boron Trifluoride Structure
Boron trifluoride, often known as trifluoroborane, is an inorganic chemical that is commonly employed as a catalyst and Lewis acid in the production of high purity boron and boron compounds.
The boron trifluoride formula is BF3. It has a molar mass of 67.805 grams per mol. Talking about the Boron trifluoride structure, the boron atom is the molecule centre and forms three simple bonds with each fluoride, exhibiting a planar-trigonal structure and a vacant p-orbital on the boron atom, similar to the boron bromide structure. The BF3 molecule likewise defies the octet of valence electron regulations. In the typical representations for organic compounds, their chemical structure can be expressed as follows.
Uses of Boron Trifluoride
Here are the Boron trifluoride uses that you must know;
- Boron trifluoride is employed in polymerization, alkylation, and condensation processes as a catalyst.
- Boron trifluoride is a highly reactive compound that is largely utilized in chemical synthesis as a catalyst.
- BF3 is the starting ingredient for several boron compounds like diborane.
- BF3 is used in the production of adhesives and sealing chemicals, as well as lubricants and lubricant additives.
Properties of Boron Trifluoride
Let’s discuss the physical and chemical properties of boron trifluoride.
1. Physical Properties:
Boron trifluoride is a poisonous gas that is colorless and has an unpleasant odor. It has a melting point of -127°C and a boiling point of -100°C, respectively. It’s density is 0.90 g mL-1. Boron trifluoride is water-soluble. Sulfuric acid and organic solvents such as benzene, carbon tetrachloride, Sulphur dioxide, and chloroform are also soluble in it.
2. Chemical Properties:
Hydrofluoric acid is formed when BF3 is gradually hydrolyzed in water. As a result of their planar-trigonal structure, boron fluoride is a nonpolar molecule with zero polar momentum. BF3 is a Lewis acid, like boron tribromide, since it is “electron-deficient” and interacts quickly with Lewis bases to produce Lewis adducts, such as in the reaction of caesium fluoride with BF3 to form caesium tetrafluoroborate:
CsF + BF3 → CsBF4
Molecular Geometry Notation for BF3 Molecule:
According to the VSEPR theory, if the BF3 molecule has such an AX3 generic formula, the molecular geometry and electron geometry will both be trigonal planar forms.
Name of Molecule | Boron trifluoride |
Chemical molecular formula | BF3 |
Molecular geometry of BF3 | Trigonal planar |
Electron geometry of BF3 | Trigonal planar |
Hybridization of BF3 | sp2 |
Bond angle (F-B-F) | 120º degree |
Total Valence electron for BF3 | 24 |
The formal charge of BF3 on boron | 0 |
Application:
Boron trifluoride (BF3) is used in a variety of products. The catalytic characteristics of BF3 as a strong Lewis acid are exploited in processes such as aromatic hydrocarbon alkylation, polymerization of phenolic and epoxy resins, and various isomerization, esterification, and condensation reactions.
It’s utilized to make high-purity boron isotopes for purposes like nuclear waste containment and neutron radiation management, as well as semiconductor industry applications like semiconductor grade silicon manufacturing.
BF3 is also utilized in the synthesis of diborane and other boron-containing chemicals, as well as a gas flux for soldering and brazing.
Health Effects/Safety Hazards
Inhalation of boron trifluoride is extremely dangerous. It wreaks havoc on the eyes and skin. BF3 reacts with water to generate hydrofluoric acid, which is extremely corrosive. When heated, it emits white poisonous fluoride gas. When it comes into contact with water, it decomposes. Plastic and rubber may be attacked by BF3.
Important Points to Remember
- In most cases, the three hybridized sp2 orbitals are organized in a triangle pattern.
- The boron trifluoride formula is BF3
- The BF3 molecule is made up of one Boron has sp2 orbitals and three Fluorine has p orbitals.
- In BF3, all of the bonds are sigma bonds. But when back bonding takes place partially double bond character shows.
Conclusion
Here, we’ve understood the structure, properties, and uses of boron trifluoride, its applications, and more.
Though a brief understanding of the topic is good when you want to clear your concepts. But if you are looking to score good marks in your IIT/JEE Mains examination, you must have an in-depth understanding and knowledge of boron trifluoride.
If you face difficulties, you may choose Unacademy to utilize live classes, recorded lectures, and notes provided by experienced tutors.
So, what are you waiting for? Dive into the pool of knowledge with Unacademy.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





