Amines are derived from ammonia. Alkyl or aryl groups replace one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia. The –NH2 group is known as the amino group. Amides have a nitrogen atom attached to the carbon of the carbonyl group. The nitrogen atom has a pair of non-bonded electrons. Amides have similar chemical properties to that of amines. Amines are further divided into three categories; aliphatic amines, aromatic amines, and heterocyclic amines. When an alkyl group is attached to the nitrogen, it is Aliphatic amine. When an aryl group is attached to the nitrogen, it is aromatic amine. When nitrogen of an amine is a part of a cyclic ring, it is a heterocyclic amine. Amines are basic in nature.
Structure of Ammonia
- Ammonia is an inorganic compound made up of nitrogen and hydrogen.
- The nitrogen being the central atom, is attached to 3 hydrogen molecules.
- The nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons.
- Amines are derived from ammonia molecules where the hydrogen molecules bound to the central nitrogen atom are replaced with different functional groups.
- Amines are called simple amines when all the aryl or alkyl groups are the same.
- Amines are called mixed amines when the aryl or alkyl groups are different.
Structure of Amines
- Amines have a nitrogen atom bonded to either aryl or alkyl group.
- Nitrogen has a valency of 5.
- The nitrogen atom has a pair of non-bonded electrons; hence the C-N-H angle in amines is less than 109 degrees giving it a tetrahedral shape.
- Nitrogen in an amine molecule is sp3 hybridised according to the VSEPR theory.
- All the sp3 hybridised nitrogen orbitals overlap with hydrogen orbitals or carbons orbitals.
- Amines have pyramidal geometry.
Classification of Amines on the Basis of Structure
Amines can be classified into three categories on the basis of the number of hydrogen atoms replaced in the ammonia molecule(NH3).
- Primary amine- 1 hydrogen molecule of ammonia molecule replaced by any functional group or aromatic ring.
H2N–CH3
- Secondary amine- 2 hydrogen molecules of ammonia replaced by any functional group or aromatic ring.
CH3–H2N–CH3
- Tertiary amine- 3 hydrogen molecules of ammonia replaced by any functional group or aromatic ring.
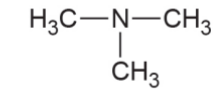
Examples of Primary Amines
- Alkyl primary amines – Isopropylamine, Methylamine
- Aryl primary amines – Aniline and its derivatives.
Example of Secondary Amines
- Alkyl secondary amines- Dipropylamine, Methylpropylamine.
- Aryl secondary amines – Diphenylamine.
Examples of Tertiary Amines
- Alkyl tertiary amines – Isopropyldimethylamine
- Aryl tertiary amines – EDTA
Biology of Amines
- In biology, amine is formed from the breakdown of amino acids.
- Amines often play the role of neurotransmitters in the body of organisms like serotonin, histamine, dopamine, etc.
- Charged amino groups in an amino acid impart a positive charge to the proteins.
Applications of Amines
- Primary aromatic amines are used in the Dye industry. It is used to manufacture azo dyes, which impart colours to different substances.
- Due to its huge abundance and importance in the body or organisms, it can be used as drugs.
- Example antihistamine drug can be used against allergic reactions.
- Many amines like monoethanolamine (MEA), diglycolamine (DGA), etc., are used to reduce the effect of greenhouse gases like Carbon dioxide. These amines are used to remove carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide from the atmosphere. It also helps in reducing air pollution.
- It can also be used in the process of water purification.
Conclusion
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia. Ammonia is an inorganic compound with a central nitrogen atom bonded to 3 hydrogen atoms. The valency of nitrogen being 5 in the structure of Ammonia or amines, it has a lone pair of electrons on it. When the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by either an aryl group, alkyl group, or a cyclic structure, it is termed as an amine. The structure of amine is classified into three categories on the basis of hydrogen atoms bonded to the central nitrogen atom. If two hydrogen atoms are bonded to the central nitrogen atom it is known as primary amine. If a single hydrogen atom is bonded to the central nitrogen atom it is known as secondary amine. If no hydrogen atom is bonded to the central nitrogen atom it is known as a tertiary amine. Amines play a crucial role in biology and have roles in air purification, water purification, and the production of dyes.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





