Introduction:
An example of a buffer solution is a water-solvent-based solution that is comprised of either a weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid, or a weak base and the conjugate acid of the weak base, in addition to a weak base. They are resistant to pH changes caused by dilution or the addition of small amounts of acid or alkali to their solution.
Adding a very small amount of strong acid or strong base to Buffer Solutions causes the pH of the solution to change by only a small amount. As a result, they are employed in order to maintain a constant pH value.
Buffer Solution
An acid-base buffer solution is a solution that can maintain its hydrogen ion concentration (pH) with only minor changes when diluted or when a small amount of acid or base is added to the solution. Buffer Solutions are used in fermentation, food preservatives, drug delivery, electroplating, printing, the activity of enzymes, and the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood. They require a specific hydrogen ion concentration to function properly (pH).
Solutions of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid, have the ability to maintain pH and are therefore known as buffer solutions.
Types of Buffer Solution
Acidic buffers and alkaline buffers are the two primary types of buffer solutions that can be broadly classified into two categories.
Acidic Buffers
These solutions, as the name implies, are used to keep acidic environments in tact and healthy. pH of an acid buffer is acidic, and it is made by mixing a weak acid and its salt with a strong base to form an acid buffer. The pH of an acetic acid and sodium acetate aqueous solution is 4.74 when the concentrations of the two acids are equal.
- The pH of these solutions is lower than seven.
- Essentially, these solutions are composed of a weak acid and a weak acid salt.
Sodium acetate and acetic acid (pH = 4.75), for example, are two acids that can be used as acidic buffer solutions.
Alkaline Buffers
These buffer solutions are used to keep the fundamental conditions in place. It is possible to create a basic buffer by mixing a weak base and its salt with a strong acid to produce a basic pH. The pH of an ammonium hydroxide and ammonium chloride aqueous solution is 9.25 when the concentrations of the two acids are equal.
Moreover, the pH of these solutions is greater than seven.
A weak base and a weak base salt are present in these formulations.
An alkaline buffer solution, such as a mixture of ammonium hydroxide and ammonium chloride (pH = 9.25), is an example of a base.
On Addition of Acid and Base
- When acid is added, the acetate ions remove the acid’s released protons, forming an acetic acid molecule.
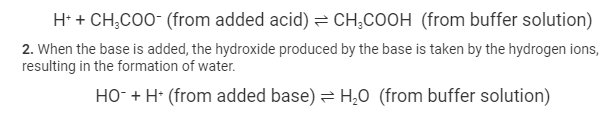
Preparation of Buffer Solution
If the dissociation constants of the acid (pKa) and the base (pKb) are known, it is possible to prepare a buffer solution by controlling the salt-acid or salt-base ratios, respectively.
This type of solution is prepared by mixing weak bases with their corresponding conjugate acids, or by mixing weak acids with their corresponding conjugate bases, as previously discussed.
A good example of this method of preparing buffer solutions is the preparation of a phosphate buffer by mixing HPO42- and H2PO4–, which is shown in the figure below. This solution maintains a pH of 7.4 at all times.
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
Preparation of Acid Buffer
An acid buffer solution containing a weak acid (HA) and its salt (KA) combined with a strong base (BB) is considered (KOH). It is possible to write down the equilibrium as:

Preparation of Base Buffer
Consider the case of a base buffer solution that contains a weak base (B) and its salt (BA) in the presence of a strong acid.
As previously stated, pOH can be calculated.
- The pOH of a basic buffer is calculated as pKb + log ([salt]/[acid]).
- The pH of a basic buffer is calculated as pKa – log ([salt]/[acid]).
Significance of Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation can be used to:
- Calculate the pH of a buffer prepared from a mixture of the salt and a weak acid/base; and
- determine the value of pKa.
- Prepare a buffer solution with the appropriate pH.
The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation has some limitations.
The Henderson – Hasselbalch equation cannot be used with strong acids or bases because of the nature of the equation.
pH Maintenance
Consider the following example of a buffer solution containing sodium acetate and acetic acid in order to better understand how buffer solutions maintain a constant pH.
This example illustrates how almost completely the sodium acetate undergoes ionisation whereas only a weak amount of ionisation occurs in the case of the acetic acid. The following is an example of an equilibrium reaction:

In the presence of strong acids, the H+ions combine with the CH3COO–ions to form a weakly ionised acetic acid, resulting in a negligible change in the pH of the surrounding environment. In the absence of strong acids, the pH of the surrounding environment remains constant.
Upon introduction of strongly alkaline substances into this buffer solution, the hydroxide ions react with the acids that are already present in the solution, resulting in the formation of water molecules. So the hydroxide ions react with the acid to form water while the pH remains unchanged.
Conclusion:
pH buffers, also known as hydrogen ion buffers, are aqueous solutions that have a traceable pH value and whose pH value changes only slightly when small amounts of acids or bases are added. pH buffers are typically composed of a conjugate base and a weak acid, which work together to absorb excess hydrogen atoms from the solution and maintain a stable pH value in solution. As a result, they are effective for calibrating electrochemical potentiometers for pH measurements with a low level of uncertainty, thereby improving traceability.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





