Ozonolysis is a chemical process in which ozone cleaves the pi bonds of unsaturated olefins such as alkenes and alkynes. It’s a bond-breaking form of cycloaddition. Ozone is an extremely reactive oxygen allotrope that easily interacts with alkenes. A carbonyl group substitutes the numerous carbon-carbon bonds in alkenes, which are organic molecules.
Ozone break the C=C bond of alkenes during this reaction, resulting in the formation of ozonide, an intermediate chemical. A reducing agent, such as zinc (Zn) or dimethyl sulphide((CH3)2S), decomposes the ozonide into carbonyl compounds. Simultaneously, the reducing agent is oxidised to zinc oxide (ZnO) or other metal oxides. This is referred to as reductive workup, and it produces aldehyde and ketone.
Ozonolysis of Alkenes
Alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids can be formed by oxidising alkenes with ozone. Ozone is bubbled through an alkene solution in methanol at 78°C until the solution takes on a characteristic blue colour from unreacted ozone in a straightforward process.
This signifies that the alkene has been completely consumed. Alternatively, by detecting the presence of ozone, several additional compounds can be employed as indicators of this endpoint. The gas that bubbles out can be routed via a potassium iodide solution if ozonolysis is done by bubbling a stream of ozone-enriched oxygen through the reaction mixture. When the solution no longer absorbs ozone, the ozone in the bubbles oxidises the iodide to iodine, which can be seen plainly by its colour.
The intermediate ozonide is subsequently converted to a carbonyl derivative using a reagent after the addition is complete. The use of reductive workup conditions is significantly more widespread than the use of oxidative work-up settings. The utilisation of aldehydes or ketones is produced when triphenylphosphine, thiourea, zinc dust, or dimethyl sulphide are used, whereas Alcohols are produced by sodium borohydride. Recently, Aldehydes have been reported to be produced directly using amine N-oxides. Ozone can also oxidise other functional groups, such as benzyl ethers. Because minor amounts of acid are produced during the reaction due to solvent oxidation, pyridine is occasionally employed to buffer the reaction.
Unsymmetrical products can be made from symmetrical alkenes by carefully manipulating the reaction/workup conditions:
- An aldehyde and a dimethyl acetal are produced using TsOH, sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), and dimethyl sulphide (DMS).
- Triethylamine (Et3N) is converted to a methyl ester and an aldehyde using acetic anhydride (Ac2O).
- A methyl ester and a dimethyl acetal are produced using TsOH; Ac2O, Et3N
Mechanism Of Ozonolysis Of Alkenes
The mechanism works in three steps, starting with an oxidative cleavage reaction with ozone. A cycloaddition process forms an unstable 5-membered ring termed a molozonide when ozone combines with an alkene. It starts with a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition but eventually ends up oxidatively cleaving pi bonds, yielding two carbonyl groups.
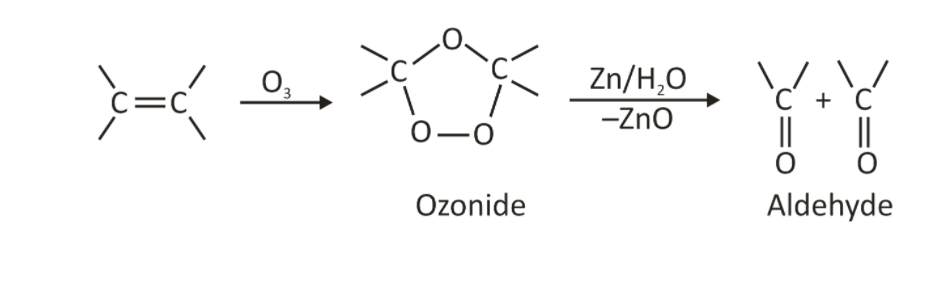
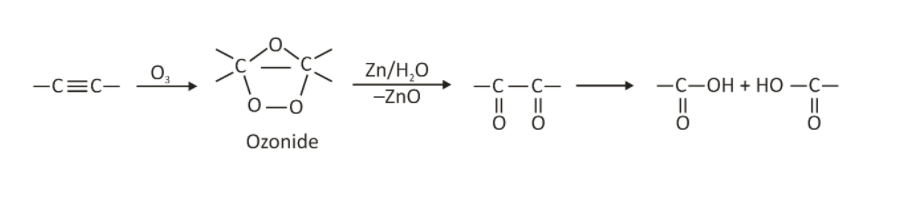
Ozonolysis of Alkynes
When alkynes are ozonized, they produce an acid anhydride or a diketone. This reaction’s fragmentation isn’t complete. Because a simple aqueous workup is used, no reducing agent is required.
Ozonolysis of Elastomers
The approach was used to identify isoprene as the structural repeat unit in natural rubber. Ozone cracking, when traces of the gas in the environment cleave double bonds in vulnerable elastomers including natural rubber, polybutadiene, Styrene-butadiene, and Nitrile rubber, is also a severe issue. Ozone cracking causes microscopic cracks in surfaces exposed to the gas at right angles to the load, which expand rapidly as the attack continues. For crack growth to occur, the rubber product must be under tension.

Application of Ozonolysis
Ozonolysis is used to determine the double bond position in alkenes and the triple bond position in alkynes. It has been widely used to determine the structure of natural compounds, particularly terpenes, as well as to synthesise uncommon aldehydes and ketones.
Conclusion
Ozonolysis is an organic chemical reaction that uses ozone to break unsaturated bonds in alkenes, alkynes, and azo compounds (compounds with the functional diazenyl functional group). It’s a redox reaction in the organic realm. Alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids can be produced by oxidising alkenes with ozone.
Alkynes are converted to acid anhydrides or diketones through ozonolysis. If there is any water present in the reaction, the acid anhydride hydrolyses to produce two carboxylic acids.
Ozonolysis, commonly known as ozone cracking, is the breakdown of elastomers by ozone. The double bonds in elastomers are cut by trace levels of ozone gas in the atmosphere.
The ozonolysis of azo compounds produces nitrosamines.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





