There are different kinds of forces, i.e., attraction and repulsion forces which are responsible for the combination of colloidal particles. The intermolecular forces between the colloidal particles play a significant role in the applications of colloids in many industrial purposes. Interaction forces support in identifying the chemical behavioural aspect of the colloids and it also explains the other important properties of sols. Let us learn more about the intermolecular forces through this article.
Definition
Any colloid is made up of a mixture of small or large molecules (particles) and a solvent (liquid). Generally, the liquid part is considered as the dispersed medium. Colloids are a type of heterogeneous mixture.
A few common examples of colloids that are found in our body are RBCs (red blood cells) which are responsible for the oxygen transfer in our body system. Another important example is milk, which is again a natural colloid. Some man-made products that consist of colloids are inks, paints, suspensions, cosmetic materials, etc.
These colloids are bound together due to various intermolecular forces. The brief related to these are mentioned below:
Interaction forces
There are many applications that are directly linked with the strength of forces in the colloidal particles. The intermolecular forces between the particles of colloids play significant roles, and many properties depend on the interaction forces. This also helps in understanding the behaviour of particles with the environmental factor.
Chronology related to interaction forces
During the 20th century, a quantitative theory, DLVO (Derjaguin-Landau-Verwey-Overbeek) theory developed, and it provided insights related to the colloidal system that it has attractive and repulsive properties between the particles of colloids. This theory states the capacity of mixing or separation of colloidal particles is dependent on the combining forces of electrostatic repulsion and van der Waals attraction.
In 1976, an apparatus called Surface Force Apparatus was developed to measure the small quantity forces on the upper side of the particles and its effectiveness on the colloidal functioning.
The different kinds of interaction forces in the colloids are as follows:
- Electrostatic force
- London – van der Waals forces
- Electrical double-layer forces
- Solvation forces
- Steric forces
- Hydrophobic forces
- Friction forces
Types of colloids
On the basis of interaction forces, the following are the types of colloids represented below:
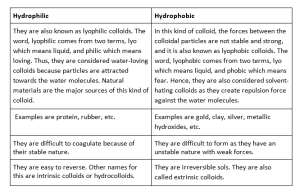
Hydrophilic colloids
They are also known as the lyophilic colloids. The word, lyophilic comes from two terms, lyo which means liquid, and philic which means loving. Thus, they are considered water-loving colloids because particles are attracted towards the water molecules.
Even after separation, the particles have the tendency to remix with the water molecules. Furthermore, they are difficult to coagulate because of their stable nature. But, there is an exception in this also, that is agar, which is reversible in nature, and by applying heat or cooling, it can be separated. Other names for this are intrinsic colloids or hydrocolloids.
Natural materials are the major sources of this kind of colloid. Examples are protein, rubber, etc. They are mainly used in the field of medicine.
Hydrophobic colloids
In this kind of colloid, the forces between the colloidal particles are not stable and strong, and it is also known as lyophobic colloids. The word, lyophobic comes from two terms, lyo which means liquid, and phobic which means fear. Hence, they are also considered solvent-hating colloids as they create repulsion force against the water molecules.
In the formation process of these colloids, more mechanisms are needed because of the tendency of particles not to attract towards the solvent material, they are unstable in nature. They are irreversible sols. They are also called extrinsic colloids. Examples are gold, clay, silver, metallic hydroxides, etc.
Conclusion
Thus, interaction forces between the particles of colloids have an important role in the formation of colloids. There is a variety of these forces that are responsible for the attraction and repulsion behaviour of particles. Colloids are prepared by different chemical processes, such as condensation or dispersion. They tend to show the Tyndall effect (scattering of light through particles present in the solvent). All colloids have two phases, i.e., a dispersed phase and a dispersion medium. On the basis of interaction forces, colloids are divided into two categories, i.e., hydrophobic and hydrophilic.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out