When two molecules bond together with electrons, they are hybridised. Organic molecules contain carbon that is bonded to other elements. Sulphur tetrafluoride is a molecule that has four atoms: one sulphur and three fluorine atoms. It is an inorganic compound because it contains no carbon, differentiating it from the hybridisation of sulphur trifluoride, sulphur hexafluoride, and sulphur pentafluoride.
What is Hybridisation?
Hybridisation is when two molecules bind together with electrons to form a new molecule.
For example, silicon (a pure element) bonds with oxygen to form a silicon compound.
Hybrids are a mixture of two or more molecules that are mixed. For example, a silicon compound called silica is half oxygen and half silicon. Hybrids all have the same chemical properties as their components.
About Sulphur Tetrafluoride
Sulphur tetrafluoride is a compound that contains four atoms: one sulphur and three fluorine atoms. This molecule has the same chemical properties as fluorine and sulphur, but it is alloyed with both elements. Sulphur tetrafluoride hydrides are a combination of elements that contain hydrogen.
For example, hydrogen (H) and sulphur (S) combine to make hydrogen sulphide. Other side effects of sulphur tetrafluoride are known as the hybridisation of sulphur tetrafluoride. Its chemical formula is SF4.
When sulphur tetrafluoride bonds with two molecules, sulphur tetrafluoride forms four atoms: two sulphur and two fluorine atoms.
Sulphur hexafluoride bonds with another substance when two molecules bind together with electrons to form a new molecule.
What is the Hybridisation of Sulphur Tetrafluoride?
The hybridisation of sulphur tetrafluoride occurs when two molecules bind together with electrons to form a new molecule.
When sulphur tetrafluoride bonds with two molecules, it forms four atoms: two sulphurs and two fluorine atoms.
The hybridisation of sulphur tetrafluoride is a chemical property of a molecule, as a chemical property of an element is based on its structure. For example, carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are soluble in water, i.e. they are water-soluble. Hybridisation, in this case, can be described as the combined formula of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen that produces carbon dioxide or CO2.
Hybridisation type in SF4: SF4 has an sp3d type of hybridisation. In a molecule of SF4, each S atom is bonded to four fluorine atoms. The S-F bonds obviously are all single bonds, and the S=F bond is the strongest bond in SF, with an estimated bond energy of 773 kJ/mol. The properties of SF are very similar to those of F.
The fluorine atoms can combine with the sulphur atoms to form a variety of σ bond combinations. These bonds are weak, and the half-life is significantly less than one hour. This “F-S” bond in SF is known as a σ bond. There are several F-S bonds in SF, but they all have similar properties.
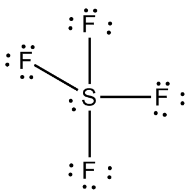
Chemical Formula and Properties of Sulphur Tetrafluoride: The chemical formula of sulphur tetrafluoride is SF4. It is an inorganic compound as it contains no carbon. The atoms in the molecule formula for sulphur and fluorine are 2 and 4, respectively. Sulphur is yellow, while fluorine has no colour. Fluorine has a very low boiling point (–188 °C) and a high melting point (–188 °F).
Atomic Mass of Sulphur Tetrafluoride: Atomic mass is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom’s nucleus. The atomic mass of sulphur tetrafluoride is 115.87.
Acid-Base Reaction Between Sulphur Tetrafluoride and Water: The acid-base reaction between sulphur tetrafluoride and water results in the formation of sulphuric acid and fluorine.
Physical properties of sulphur tetrafluoride: Sulphur tetrafluoride is found in the form of a gas or liquid, which is colourless to yellow. Its density is 1.96 g/cm3, which means that it has a gravity of –0.735 compared to water which is 1 g/cm3 and has a gravity of 1.000.
Sulphur tetrafluoride is a liquid when it is over pressurised and gas when it is under pressure. Sulphur tetrafluoride and hydrogen are linearly chirally equivalent. It can not be decomposed.
Conclusion
The above article has given us a great amount of information about the hybridisation of sulphur tetrafluoride. Inorganic compounds are very interesting because they have the same chemical properties as their parent elements, but they can bond with other elements to create different structures. Many different compounds have sulphur tetrafluoride. Sulphur tetrafluoride is an inorganic compound with a very high boiling point (–188 °C) and a low melting point (–188 °F).
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





