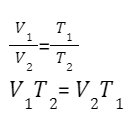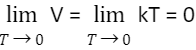Jacques Charles discovered in 1787 that given a fixed amount of gas, the volume of a gas sample rises linearly with temperature if the pressure is kept constant. Temperature was born as a result of this law. Kelvin is the temperature measurement unit. According to Charles’s law:
The volume of an ideal gas is proportional to the absolute temperature at constant pressure. Simply expressed, when the pressure on a dry gas sample is held constant, the Kelvin temperature and volume will be in direct proportion.
What is Charles’s Law?
Charles’s Law, often known as the law of volumes, describes how a gas expands as the temperature rises. A reduction in temperature, on the other hand, will result in a decrease in volume. When comparing a substance under two different situations, we can write the following from the above statement:

As a result, V = kT. The law is frequently expressed as V = kT when comparing an equivalent substance under two different sets of circumstances.
This equation shows that when the absolute temperature of the gas rises, the volume of the gas rises in proportion. To put it another way, Charles’s law is a variant of the ideal gas law. The law applies to ideal gases that are kept at a constant pressure but have varying temperatures and volumes.
At a given temperature (266.66 °C, according to Gay-numbers) Lussac’s or 273.15 °C, Charles’s law appears to imply that the quantity of gas will decrease to zero. Because the gas has no energy at room temperature, the molecules are unable to move. According to Charles’s studies, the quantity of a hard and fast amount of a gas grows or drops by 1273 (now 1273.15) times the quantity at 0°C for each 1°C rise or fall in temperature under constant pressure.
Graph-
A volume vs. temperature graph plotted as a constant pressure for a specific amount of gas is shown below. As can be seen from the graph, volume increases as temperature rises, and vice versa. As a result, at constant pressure, volume is directly proportional to temperature, as stated by Charles’s law.
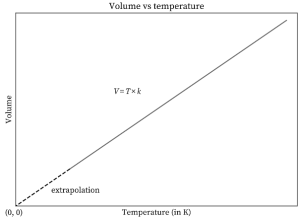
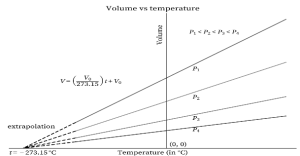
The y-axis represents volume, whereas the x-axis represents temperature. The graph is a straight line travelling through the origin with a positive slope. The line’s equation is V = kT, which is Charles’ law’s equation. The line has a slope of k. As the temperature approaches 0 kelvin, so does the volume. The volume of an ideal gas at 0 kelvin is also zero, according to the graph.
The charts below can be plotted at various pressures. Four separate lines can be seen in the graphs below. The lines are all at the same pressure. Isobars are such lines that are drawn at a constant pressure.
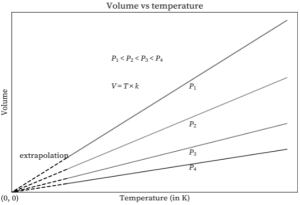
As the temperature approaches zero, each of the lines converges at zero volume. Additionally, the lines slide inwards with increased pressure, if detected (towards the x-axis). This is due to a drop in the value of k as pressure increases. The same is true in the diagram below, except that each line converges at 273.15 °C.
Daily Life Example
Hot Air Balloon – An air balloon works on a fundamental basis. It is made up of a bag or an envelope, a passenger basket, and a fuel supply such as propane. The air inside the envelope heats up when the fuel is ignited. According to Charles’s law, hot air expands. As the temperature of the air rises, the volume of the air rises as well, resulting in a drop in density. As a result, the envelope is lighter than the air surrounding it. The lighter envelope is propelled into the air by the buoyant force, and it flies.
Human Lungs – The lungs are spongy air-filled organs that serve a critical role in respiration. When the lungs expand, air comes in, and when they contract, air flows out. The temperature of the air drops in winter. As a result, the temperature of the air inside the body drops as well. Volume is directly proportional to temperature, according to Charles’s law. As a result, as the temperature rises, the volume of air decreases. It causes the lungs to shrink, making physical activity such as jogging difficult on cold winter days.
Pool Floats – We’ve all used a pool float as a kid during swimming training. Air is used to fill pool floats, making them significantly less dense than water. Because the temperature of the air inside swim floats drops, the air inside shrinks. During hot summer days, when the water is significantly warmer, the opposite behaviour is displayed. When the temperature of the air inside swim floats rises in a hot area, they get overinflated.
Conclusion
The law of volumes is another name for Charles’s law. The relationship between a gas’s volume and temperature is described by the law. It does, however, have certain limitations in that it only applies to perfect gases. It is good for actual gases at high temperatures and low pressures at the same time.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out