As we know, a cell consists of two electrodes: an anode and a cathode. The Anode is positively charged and the cathode is negatively charged so there is a separation of charge; this charge separation results in generation of a potential difference, this potential difference is called cell potential or voltage. It is also called emf of the cell. This cell potential generates / flows current in a cell.
To study cell potential; first we need to learn some terms related to a cell.
CELL: There are two types of cell:
Electrochemical cell and Electrolytic cell. In electrolytic cells, we give / apply voltage to the cell. So, the voltage of an electrolytic cell will be the voltage of the applied electricity. But in an electrochemical cell, the voltage is generated in the cell. So: we generally study the cell potential or voltage of the electrochemical cell. Oxidation of the metal electrode takes place at the anode and reduction takes place at the cathode.
Electrode Potential: A cell has two electrodes anode and cathode they are made up of metals so when the circuit is complete the metal at anode starts losing electrons and the metal at cathode starts gaining electrons. As a result of this transfer of electrons, a charge separation occurs at both the electrodes. This charge separation generates potential at both the electrodes. The potential generated at each electrode is called electrode potential. Electrode potential of a half cell can be determined by using a Standard Hydrogen Electrode. Because the half cell potential of SHE is 0V.
Standard Electrode Potential: Standard electrode potential is the electrode potential of a given electrode at a unit concentration, i.e, 1 mole at 1 ATM pressure and 25℃. The standard reduction potential is the standard electrode potential of the cell because the reduction potential is equal to the oxidation potential; but the oxidation potential is negatively charged.
Cell Potential: The difference in potential difference generated at both the electrodes is called cell potential. In general the difference between the potential difference of the potential generated at each half cell is called cell potential.
E⁰cell = E⁰cathode – E⁰anode
Ecell > 0 for a spontaneous process
Cell potential is also called the emf of the cell. It is measured in Volts(V).
EMF = Reduction potential of cathode – Reduction potential of anode
Cell Potential is also related to Gibbs free energy.
∆G = -nEcellF
Calculation of EMF of the cell:
Taking daniell cell for calculation of emf
For 1 molar concentration the standard electrode potential of half cell reactions
At cathode Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu is equal to E⁰cathode = 0.34 V.
At anode Zn → Zn2+ + 2e– is equal to E⁰anode = -0.76 V.
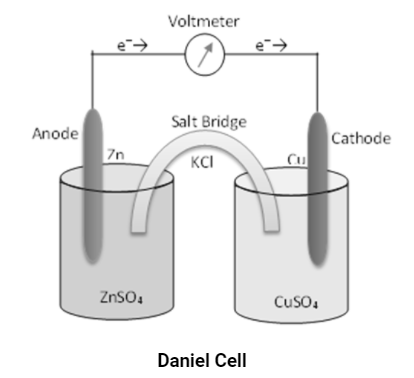
The complete cell reaction of the Daniel cell is
Zn + Cu2+ ⇌ Zn2+ + Cu
The emf of the cell is
E⁰cell = E⁰cathode – E⁰anode
E⁰cell = 0.34V – (-0.76)V
E⁰cell = 1.1V
Standard Electrode Potential of Some Cells
Half Cell Reaction | Standard Electrode Potential |
F2(g) + 2e– ⇌ 2F–(aq) | 2.87 |
Al3+(aq) + 3e– ⇌ Al(s) | -1.67 |
2H+(aq) + 2e– ⇌ H2(g) | 0.00 |
AgBr(s) + e−⇌ Ag(s) + Br− | 0.80 |
H2O2(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2e– ⇌ 2H2O(l) | 1.78 |
Fe2+(aq) + 2e– ⇌ Fe(s) | -0.44 |
PbSO4(s) + 2e−⇌ Pb(s) + SO42− | -0.13 |
Nernst Equation for emf of cell:
Ecell = Ecell – (RT/nF) ln Q
Ecell = cell potential
Eocell = standard state cell potential
R = universal gas constant (8.31 J/mol K)
T = absolute temperature (in Kelvin)
F = Faraday’s constant (96,485 C/mole e–)
n = number of moles of electrons transferred in the cell
Q = reaction quotient
At constant temperature 25℃.
Ecell = Ecell – (0.0257/n) ln Q
or in terms of log10
Ecell = Eocell – (0.0592/n) log Q
Conclusion:
In this topic we studied cell potential or emf of the cell and its determination with the help of cell potential we can determine how much current an electrochemical cell or battery can produce. Cell potential also helps us in determining which metal electrodes are good for the construction of a cell.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





