The relationship between the volume of a gas and its pressure was named Boyle’s law after Robert Boyle, who was an Irish scientist. He was the first to research the quantitative link between a gas’ volume and pressure in 1962. Robert Boyle was also an eminent natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, and inventor.
Meaning of Boyle’s Law
The law states that the degree of a given amount of gas at a continuing temperature is reciprocally proportional to its pressure. As a result of the gas particles being loosely packed in nature, they can move around freely in their surroundings. When a container is packed with gas, the gas molecules tend to hit the boundary of the container while moving around.
Once the container’ volume is lowered, the gas particles will touch the container’s boundary a lot more, thereby increasing the pressure. In the same way, when the volume of the container is increased, the pressure of the gas drops. Robert Boyle discovered that once a compressive force is applied to a gas in a container, the gas behaves like a spring and resists the compressive force.
If the volume of a certain amount of gas at constant temperature T is V and the pressure is P, then according to Boyle’s law,

where k is a constant whose value is determined by the volume of the gas V and its temperature P.
According to Boyle’s law, the product of the volume and pressure of a given amount of gas at a certain temperature is constant based on the preceding equation.
Let T be the temperature and P2 be the pressure of a particular quantity of gas. Now, if the gas’s pressure at temperature T is increased to V2, resulting in a volume V2, according to Boyle’s law, the gas’s volume will be V2.
P1 V1 = P2V2
They are constants, when mass and temperature are constant.
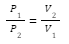
P1= Initial pressure exerted by the gas
P2= Final pressure exerted by the gas
V1= Initial volume occupied by the gas
V2= Final volume occupied by the gas
Examples of Boyle’s law
Respiration: Our lungs use Boyle’s law during respiration. When you breathe in, your lungs expand because they are filled with air. As the volume increases, the pressure level decreases. Similarly, when air is deflated, the lungs contract, reducing volume and increasing pressure. The change in pressure and volume is both instantaneous and periodic.
Soda bottle: One of the best examples of Boyle’s law is a soda bottle filled with a mixture of carbon dioxide and water. It is difficult to squeeze a sealed beverage can or container. This is because the air molecules inside the container are tightly packed and have little room to move. When you open a can or bottle, some air molecules leave the container, allowing room for more air molecules to move in and squeeze the bottle. The change in pressure as a function of the volume can be clearly seen in this example.
Scuba diving: When diving underwater, it is important to ensure that the volume and pressure ratios are balanced to avoid illness or injury. You feel great pressure when entering or approaching the depth of the body of water. The solubility of gases in the human blood increases with high pressure. As it rises or moves up, the pressure in the blood begins to drop, and the gases in the blood begin to expand. As a result, the diver must ascend slowly to avoid damage. Boyle’s law is based on the relationship between pressure and volume.
Graphical representation of Boyle’s law
A direct line going via the starting place for a plot of P vs 1/V at a steady temperature for a fixed quantity of fuel line might be a graphical illustration of Boyle’s Law.
A rectangular hyperbola is a plot of P vs V at constant temperature for a specific mass of gas.
A straight line parallel to the PV axis is used to plot P (or V) versus PV at constant temperature for a specific mass of a gas.
Conclusion
Boyle’s law regulation is very important as it explains how gases behave. It proves past a shadow of a doubt that fuel line strain and quantity are inversely proportional. When you press down on a fuel line, the quantity shrinks, and the strain rises.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





