Aluminium oxide is also known as alumina, and its chemical formula is Al2O3. It is sometimes also known as alundum, aloxide, or aloxite. It is an amorphous material, has no odour, appears white, and is inert. This compound is insoluble in water and thermally unstable. Also, it reacts with both acid and bases alike; therefore, it is amphoteric. In nature, alumina can be found naturally in corundum, sapphire, emerald, and ruby. An everyday use of alumina is its applications in industrial ceramics. Also, it is used in cutting tools and as an abrasive due to its hardness.
Preparation of aluminium oxide
Bayer’s process is used to produce alumina. This process involves the following steps:
- Digestion – The bauxite ore (Al2O3.2H2O) is crushed and heated with caustic soda (NaOH). This solution is heated for 2-8 hours at 140-150C under high pressure. The tank in which it is heated is termed a digester. Since alumina is amphoteric in nature, it reacts with the aqueous NaOH solution to form sodium aluminate. The reaction for this step can be illustrated as follows:
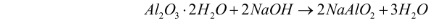
- Filtration – Bauxite includes other components apart from alumina, which does not dissolve in caustic acid. The undissolved components settle down at the bottom of the digester as red mud. This mud is removed through filtration.
- Precipitation – Aluminium hydroxide is obtained as a precipitate when the sodium aluminate solution (NaAlO2) is diluted with water, and the mixture is then cooled to 50C. The reaction for this step can be illustrated as follows:
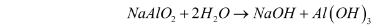
- Calcination – The aluminium hydroxide obtained from the previous step is filtered, washed, dried, and then heated at 1010-1260C in calciners. This gives aluminium oxide. The reaction for this step can be illustrated as follows:
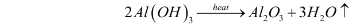
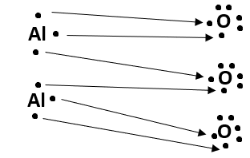
Structure
The structure of alumina consists of two aluminium atoms and three oxygen atoms. Each aluminium atom loses three electrons to gain a positive charge of +3, and each oxygen atom gains two electrons to acquire a negative charge of -2. This forms an ionic compound, since a metal (aluminium) loses electrons to a non-metal (oxygen). The dot structure of Al2O3 can be illustrated as follows:
Physical properties
The physical properties of aluminium oxide are as follows:
- It has a molar mass of 101.96 g·mol−1
- It has a boiling point of 2,977 °C.
- It has a density of 3.95–4.1 g/cm3.
- It is a hard material.
- It is resistant to electricity.
- It has low thermal expansion.
- It has corrosion endurance.
Chemical properties
- Reaction with water – The oxide ions in Al2O3 are held strongly and therefore do not react with water. This makes Al2O3 insoluble in water.
- Reaction with acids – Al2O3 reacts with acids due to the presence of oxide ions. For example, when it reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, it gives aluminium chloride and water. When reacting with an acid, it acts as a base.
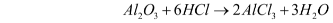
- Reaction with bases – Al2O3 also reacts with bases. When reacting with bases, it acts as an acid. For example, when it reacts with sodium hydroxide, it forms sodium aluminate and water.
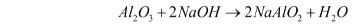
Uses
Alumina is used in the following fields:
- Medical industry – In medicine, alumina is used as a material for hip replacement bearings, in tissue reinforcement, as prostheses, in bionic implants, in dental implants, in lab equipment like furnaces and crucibles, etc. The reason for the use of alumina in the medical industry is its hardness and bio-inertness.
- Military and protective equipment – Alumina is used in some military equipment, like body armour. It is also used in protective equipment like aircraft armour, vehicle armour, and bulletproof windows. This is due to its lightweight qualities and strength.
- Electronics industry – Alumina is used to manufacture electrical insulators and furnace insulation. This is because of its high melting and boiling points. It is also used in the microchip industry in the form of alumina films. Some other applications of alumina in the electronic industry include insulating heatsinks, spark plug insulators, and micro-electric substrates.
- Gem industry – The crystalline form of alumina, corundum is the base element for rubies and sapphires. Both rubies and sapphires are precious gems. They get their colour from trace impurities. Rubies get their colour from chromium while sapphires get their colour from iron and titanium.
- Industrial applications – Alumina is used as an abrasive for sandpaper owing to its strength. It is also used as a filler in bricks, clayware and plastics due to its inert nature. It is also a substitute for diamond as a more economical option. It can be an ingredient in toothpaste and sunscreen.
Conclusion
Aluminium oxide is also known as alumina, and its chemical formula is Al2O3. Its structure consists of two aluminium atoms and three oxygen atoms. Each aluminium atom loses three electrons, thereby gaining a +3 charge, and each oxygen atom gains two electrons, thereby gaining a -2 charge.
Alumina can be prepared through Bayer’s process. In this process, bauxite (ore of aluminium) is heated with caustic soda (NaOH). Sodium aluminate (NaAlO2) is obtained in this process, which, when diluted with water, gives aluminium hydroxide (Al(OH)3). When aluminium hydroxide is heated, aluminium oxide and water vapour are obtained.
Alumina has a high melting and boiling point, is resistant to electricity, and is insoluble in water. It is amphoteric in nature, i.e. it reacts with acids and bases alike. It is used in the medical industry, the electronic industry, the gem industry, the manufacture of protective equipment, etc.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





