An aldehyde is indeed an organic molecule with a carbonyl group by the end. The functional group, known as just an aldehyde group, is either a carbon atom with such a single covalent link to something like a hydrogen atom or a double bond to that of an oxygen atom. An aldehyde functionality group’s chemical equation is -CH=O, whereas an aldehyde‘s structural formula is R-CH=O. Sometimes, the aldehyde point is called the formyl and methanol groups. Ketones and carboxylic acids are more examples of organic molecules with carbonyl groups. In chemical synthesis, an aldehyde is indeed a similar application group. Fragrance oils, and also organic and inorganic hormones, include aldehydes.
Aldehydes
Apart from formaldehyde, most aldehydes also have a carbonyl group on a single side connected to hydrogen as well as alkyl and otherwise aryl group on either. The commonest aldehyde is formaldehyde, which possesses hydrogen from both sides of the carbonyl group.
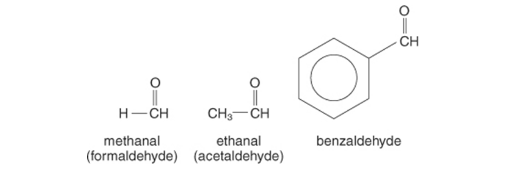
Nomenclature
The standard method or perhaps the IUPAC system is used to name aldehydes. The familiar words of aldehydes have been obtained from the carboxylic acid’s common ones. Consider the following scenario:
The IUPAC system follows a set of rules to create compound identities. Basic rules for naming aliphatic aldehydes are as follows:
- Locate the carbonyl group inside the longest-running chain of carbon atoms.
- The alkane name with the same amount of carbons is used as the parent name.
- Remove thee from the alkane title and replace it with al.
- Assign the lowest possible number to the carbonyl carbon, mainly in the chain.
- Identify and name substitutes.
The following are some examples of IUPAC naming:

The term carbaldehyde is added to the designation of the ring structure in the IUPAC system to identify cyclic, aliphatic, & aromatic aldehydes.
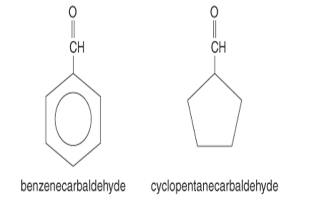
Rather than benzenecarbaldehyde, the majority of chemists call it benzaldehyde. This alternative term is also used in many sources, such as articles.
Chemicals Formula
RCHO is the chemical formula for such an aldehyde. R stands for a hydrogen ion or a carbon/hydrogen string, CO again for carbonyl and H for the hydrogen connected to the carbonyl sequence in this formula. It’s crucial to state the equation in this order because it builds the link between the aldehydic hydrogen and the carbonyl.
Aldehyde physical characteristics
Aldehydes belong to organic chemical compounds whose general balanced equation is R-CHO. R can be hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbon revolutionary.
Several aldehydes seem to be unpredictable, flammable liquids producing vapour in explosive quantities at room temperature. Lesser aldehyde components, as well as those with an unsaturated and replaced chain, need the most stringent fire and explosion prevention measures, as well as the most extensive irritating property precautions.
Aldehyde Applications
- Formaldehyde is utilised as a cleanser and organic specimen preservation.
- Glasses are silvered with an aldehyde.
- Formaldehyde is a chemical used to make a wide range of polymers and resins.
- Fragrance and the dyes (colour) business both utilise benzaldehyde.
Aldehyde Applications
1.Antioxidant
Formalin is a chemical that is used to preserve biological and anatomical specimens. This is a popular method of specimen storage at major research institutes. It is used to clean medical instruments.
2.Producing polymeric goods
Have you ever wondered why germicides, insecticides, & fungicides, among other polymeric goods, are being used to keep bacteria, bugs, and fungus at bay? This is due to the formaldehyde element employed in manufacturing these items.
3.Antiseptic
Due to its powerful ingredients, it reacts to cleanse water. Tissues are also hardened by formalin.
4.Paper-making
Acrolein is a necessary component in the paper industry since it regulates its slime.
5.Bacterial Elimination
This compound kills bacteria found in oil wells & chilled water tanks.
6.Preservative
Acetaldehyde is a flavouring ingredient and a preservative for fruits and seafood.
7.Rubber & Tire Manufacturing
Solvents containing benzene are appropriate to be used in the rubber production process.
8.Printing/painting
Because benzene is included in base & overcoat paints, it is commonly employed in the printing industry to repair and sanitise printing equipment.
9.Chemicals/Plastics
Benzyne is a chemical used to create plastics and synthetic materials such as nylon. Benzene is used in several ways in the plastics industry, such as cleansers.
10.Petroleum/Oil/Asphalt
Aldehyde is a chemical that is used to make petroleum products like gasoline. It is used to produce asphalt, which roofing firms utilise.
Conclusion
Aldehydes seem to be organic molecules with a carbon atom at the end. Because CHO is one of their main components, these are classified as compounds that contain CHO. Dehydrogenation of alcohol removes the hydrogen ion from the oxygen molecule, resulting in aldehydes. The carbon subsequently forms a double bond as a result of the reaction. Aldehydes are commonly utilised in industry to manufacture other chemicals. Aldehydes are used in various methods, many prevalent in a wide range of industries. Aldehydes are classified into four categories. Acrolein, Acetaldehyde, and Benzaldehyde are all forms of formaldehyde, which are carbon molecules, oxygen, and carbon.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





