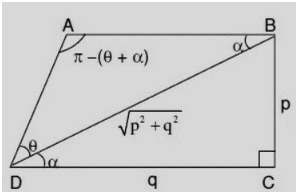
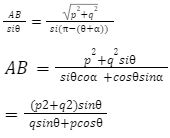A trapezoid is a four-sided quadrilateral with at least two parallel sides. It’s a planar geometric figure in two dimensions. The area of a trapezoid equals half the sum of the parallel sides’ lengths multiplied by the perpendicular distance between them. The perimeter of a trapezoid can be computed by adding the lengths of the sides together.
Significance of trapezium
Quadrilaterals have extremely influencing features that benefited ancient painters, architects, and designers in the discovery of several things in the fields of art, design, and architecture. The Egyptians used the principle of the diagonal of a rectangle generating two congruent triangles to build The Great Pyramid. Similarly, Leonardo Da Vinci employed this principle of congruency to produce his most famous picture, “Monalisa.” There are a variety of additional irregular quadrilaterals that can be used to make things appear nice. As a result, designers are the ones who use them the most.
Another quadrilateral with a wide base and narrower top, or vice versa, is the trapezium. Such shapes are extremely important in the fields of architecture and building construction. There are a variety of additional irregular quadrilaterals that can be used to make things appear nice. As a result, designers are the ones who use them the most.
Examples of trapezium
Here’s a list of places where trapeziums can be found in real life. Look around the next time you’re out and about, or even at home, to see if you can find any:
Roofs: If you look up at your roof from outside your house, it’s very likely that it’s shaped like a trapezium. If you’re drawing a house, you’ll almost certainly draw the roof in the same way.
Bags: A lot of handbags are intended to look like trapeziums. The longer bottom and shorter top make it easier and safer to store items inside.
Bridges: Take a moment to visualize yourself crossing a bridge from the side the next time you’re crossing one.
Cinema: Take a glance in your popcorn bucket the next time you’re going to the movies. It’s also shaped like a trapezium, which I’m sure you didn’t notice!
Home: There are many trapezium-shaped items in your home, including those you might not have considered. Lamp shades are a wonderful example of this, if you look closely and imagine them to be on a paper, you’ll see it.
Guitar: Chris Martin’s trapezoid custom guitars became highly popular. There are still a few spots where you can observe trapezoid guitars.
Boat: In real life, gazing at the base of a paper boat reveals the trapezoid shape. Some vessels used for water transportation are trapezoidal in design as well.
Properties of trapezium
The trapezium rule, in which the area under the curve is divided into varying numbers of trapeziums. It is critical to accurately measure the size, shape, volume, and other features of a shape when considering different applications.
Each quadrilateral has its unique set of characteristics that distinguish it from the others. These properties provide more information about a shape’s geometrical construction. The properties of trapezium are as follows:
- It’s a two-dimensional shape.
- A trapezium’s bases are parallel to each-other.
- Both diagonals have the same length.
- Both diagonals of a trapezium intersect one other.
- A trapezium’s diagonals always bisect each other.
- The total of the internal adjacent angles is 180°.
- In a trapezium, the sum of all internal angles is equal to 360° in every condition.
Conclusion
A trapezium is a four-sided closed shape with one pair of parallel sides facing each other and the other pair of sides that are not parallel. It’s a quadrilateral with four sides, four angles, and four vertices that’s convex in shape. The total summation of angles present on the inside is 360 degrees. The angle between neighboring sides is 180 degrees, and the diagonals of this structure are bisected. The height of the trapezium, on the other hand, is the perpendicular distance between two parallel lines.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out