In the Cube and Dice logical reasoning section, it says, “A cube is a three-dimensional solid object with six square faces or surfaces. It is also called a “regular hexahedron.” Dice, on the other hand, are cube- or cuboid-shaped objects with numbers, pictures, or symbols printed on them. Dice are used in games like craps, ludo, and others that don’t involve gambling.
Several different types of questions based on cube and dice reasoning are often asked in competitive tests. In this article, we’ll talk about the most important ideas in the Cube and Dice reasoning section, as well as give examples, practise questions, tips, and tricks, etc. Read the whole article to find out everything you need to know about it.
What is Cube and Dice?
As was already said, a cube is a three-dimensional shape that can only be made from squares. If you give a square the same height as one of its sides, it becomes a cube. Die is a three-dimensional object with six sides that have different numbers, letters, colours, etc. on each side. It has 12 sides and 8 corners. The length, width, and height of a dice are all the same.
In many government exams, there are sections on “Cube and Dice Reasoning.” Here are some of the types of problems you might see in those sections.
Types of Cube and Dice Reasoning
As we now know what kind of questions are on the Cube and Dice section, we can answer them better. Let’s look at the different kinds of questions that could come up, one at a time.
- Problem based on Single Dice
In this type of cube and dice reasoning, you will be given problems that involve a single die.
2.A problem based on two or more dice
In this type of cube and dice reasoning, you will be given problems that involve two or more dice.
How to Answer Cube and Dice Questions – Learn all the tricks and tips
Below are some tips and tricks that candidates can use to answer questions in the Cube and Dice Reasoning section.
Tip #1: The length, width, and height of a cube are all the same. Six surfaces, twelve edges, and eight corners make up the whole.
Tip #2: A cuboid’s length, width, and height are not all the same.
Tip #3: Common dice and standard dice are two types of dice.
Tip #4: It is a regular cube with dots numbered from 1 to 6 on each of its six sides. The numbers on the opposite sides add up to 7.
Tip #5: Always “6 is opposite to 1,” “5 is opposite to 2,” and “4 is opposite to 3” when using standard dice.
Tip #6: The sum of any two adjacent numbers on a regular dice is 7.
Cubes and Dice formula
Euler’s formula = F + V = E + 2
Important Formula
The number of small cubes is = n³
Where n = number of rows and/or columns
1 side coloured small cubes =6 (n – 2)²
2 sides coloured small cubes =12 (n – 2)²
8 small coloured cubes with 3 sides
Small coloured cubes with 4 sides = 0
Cubes that can’t be seen = (n – 2)³
Practice Questions for Dice Reasoning:
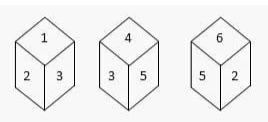
Q1. There are numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 on each of the six sides of a dice. This die is rolled three times, and the three spots are:
Find the number that goes against 1.
A. 2
B. 6
C. 5
D. 4
Answer and Reason
Solved: Choice C
Figures (ii) and (iii) show that the numbers 2, 4, 3, and 6 are all close to the letter “5”. So, the number 1 appears next to the number 5. In other words, 5 seems to go against 1.
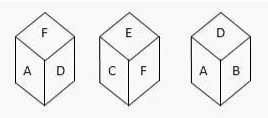
Q.2 You have three dice positions. Which face is the opposite of the face with the letter B?
A. E
B. F
C. D
D. A
Answer and Reason
Solved: Choice B
Figures I and (ii) show that the letters C, D, A, and E are right next to the letter F. So, the letter B is opposite the letter F, and the letter F is opposite the letter B.
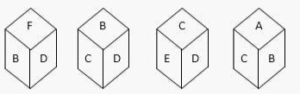
Q.3. Which face is the opposite of the face with the letter B if the four positions are as follows?
A. B
B. A
C. F
D. E
Answer and Reason
Solved: Choice D
Figures I (ii), and (iv) show that F, D, C, and A are all close to B. So, E must be across from B.
Directions for questions: Here are six different ways to set up dice:
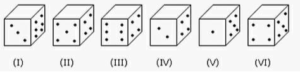
The number of dots on the other side adds up to 7.
Q4. If the top faces of dice with even numbers have an odd number of dots, how many dots are on the top faces of all the dice?
- 22
- 3
- 10
- 24
Answer and Reason
Solved: Choice B
(II), (IV), and (VI) are all even-numbered dice (VI)
How many dots are on the top side of (II) dice?
How many dots are on the top side of a (IV) die = 1
How many dots are on the top side of a (VI) die = 1
So, the total needed is 1 + 1 + 1 = 3.
Q5: If a dice with an odd number has an odd number of dots on its top face, how many dots are on the top faces of all the dice?
A. 11
B. 12
C. 13
D. 14
Answer and Reason
Solved: Choice C
(II), (III), and (IV) are all odd-numbered dice (V)
The top sides of these dice have 5, 5, and 3 dots, respectively.
Total needed = 5+5+3 = 13
Conclusion
In the Cube and Dice logical reasoning section, it says, “A cube is a three-dimensional solid object with six square faces or surfaces. It is also called a “regular hexahedron.” Dice, on the other hand, are cube- or cuboid-shaped objects with numbers, pictures, or symbols printed on them. Dice are used in games like craps, ludo, and others that don’t involve gambling.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out