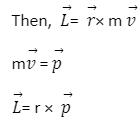As we know, the mass times the velocity of a moving object is known as momentum. Any object which has mass can produce momentum while moving. The difference between momentum and angular momentum is if an object is moving on or around a fixed axis, then it will create angular momentum.
Let’s take an example: Have you ever tried to balance your bicycle or motorcycle while still in a place? If you did, then you know that it’s not possible for more than a few seconds.
Then how does a bicycle balance when we ride it? The key to the balancing of a bike while riding is angular momentum. When you start your bike and accelerate it to produce motion, then the wheels of the bike start rotating on a fixed axis. The rotation of the wheels on that fixed axis creates the angular momentum. Moreover, this angular momentum helps the bike to balance by resisting any change to the balance.
Definition of Angular Momentum
Angular momentum is the virtue of an object rotating on a fixed axis. The angular momentum is the result of the product of the angular velocity of the object and the moment of inertia.
Angular momentum has direction as well as magnitude. Hence, angular momentum is a vector quantity. The notation of the angular velocity is a vector on L.
The SI unit of angular momentum is Kg.m².1/s. Hence, the Dimensional formula of the Angular Momentum is [L]²[T]–¹.
The formula of Angular Momentum
Point object: A point object rotating around a fixed point on a fixed axis. Example: a planet revolving around the sun.

Extended object: An object rotating on a fixed point on a fixed axis. Example: Tire of a bicycle rotating on its axis.
Right Hand Rule
The right-hand rule to identify the direction of the angular momentum is very similar to the rule which we use to get the direction of the magnetic fields in an electromagnet.
The rule states that if you curl the fingers of your right hand in the direction of rotation. And open your thumb perpendicular to your fingers. Then, your thumb will show the direction of the angular momentum.
Angular Momentum of a Satellite Meaning
According to the motion of a Satellite, it falls in the group of the angular momentum by a point object around a fixed point.
To derive a formula to calculate the angular momentum of a Satellite.
According to the second law of Newton,

We can say the application of a force around the axis generates a rate of change of momentum. Besides, we can also say that the left side of the equation is torque. Also, the quantity which is on the right of the equation is angular momentum.
Solved Angular Momentum of a Satellite questions
Q. If L is the angular momentum of a satellite revolving around the earth in a circular orbit of radius r with speed V, then L is directly proportional to it?
L=r×p
In circular orbit,
r×p = rp = mvr
∴L=√GmMr
or, L∝√r
Q. A satellite of mass m is revolving around the earth in a fixed circular orbit of radius r. Derive an expression for angular momentum.
The orbital speed of a satellite revolving around the earth in a circular orbit of radius r is,
v⁰ = √GM/r
Therefore the angular momentum of satellite,
L= mv⁰r =mr × √GM/r
=√GMm³r
Q. The orbital angular momentum of a satellite revolving at a distance r from the centre is L. If the distance increases to 16r, then new angular momentum will be.
Angular momentum
L = √m²GMr
∴L ∝√r
Then,
L²/L¹ = √r²/r¹ = √16r/r =4
L² = 4L¹ = 4L
Conclusion
This was a brief introduction to the angular momentum of a satellite. Basically, it concludes that the angular momentum of a Satellite can be derived from the second law of Newton. Moreover, the angular momentum of the satellite is the same as the angular momentum of a point object revolving around a fixed point. As we learnt today, angular momentum is a vector quantity which means it contains both direction and magnitude. So you can easily find the direction of angular momentum of an object rotating on its own axis with the help of the right-hand rule given above. Best of luck, keep preparing.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out